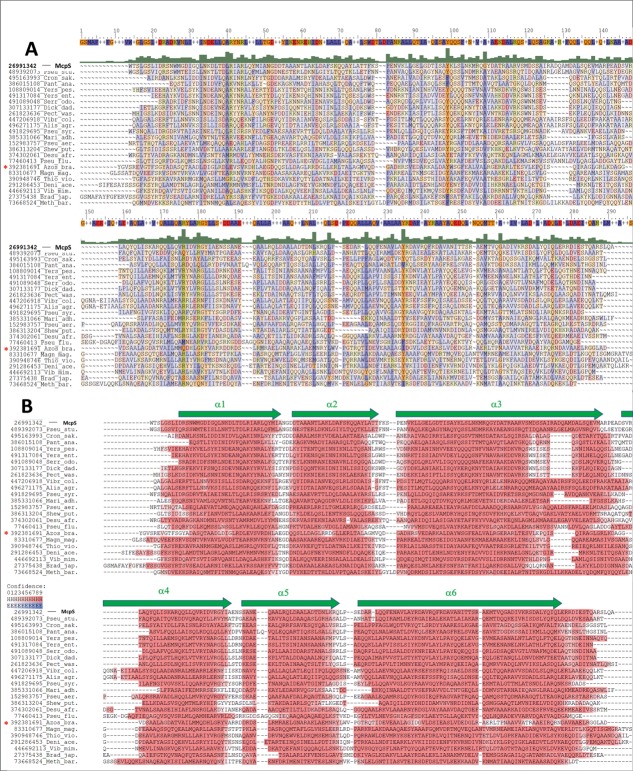
Figure 1.
Alignment of a representative subset of HBM domain sequences from chemoreceptors and a sensor kinase. The asterisk marks the sensor kinase, the remaining sequences are from chemoreceptors. Sequences were selected to cover the phylogenetic distribution of species with HBM domains. The GI numbers from the NCBI database are indicated. Alis_agr: Alishewanella agri; Azos_lip: Azospirillum lipoferum; Brad_jap; Bradyrhizobium japonicum; Cron_sak: Cronobacter sakazakii; Deni_ace: Denitrovibrio acetiphilus; Desu_afr: Desulfovibrio africanus; Dick_dad: Dickeya dadantii; Magn_mag: Magnetospirillum magneticum; Mari_adh: Marinobacter adhaerens; Meth_bar: Methanosarcina barkeri; Pan_ana: Pantoea ananas; Pect_was: Pectobacterium wasabiae; Pseu_aer: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Pseu_flu: Pseudomonas fluorescens; Pseu_stu: Pseudomonas stutzeri; Pseu_syr: Pseudomonas syringae; Serr_odo: Serratia odorifera; Shew_put: Shewanella putrefasciens;Thio_vio: Thiocystis violascens; Vibr_cho: Vibrio cholerae; Vibr_mim: Vibrio mimicus;Yers_ent: Yersinia enterocolitica; Yers_pes: Yersinia pestis (A). ClustalX alignment highlighting conserved residues: blue for hydrophobic residues (ACFILMPVW), red for acidic residues (DE), green-yellow for basic amino acids (HKR) and orange for the remaining residues (GNQSTY). The consensus sequence is shown on top of the alignment. (B). Secondary structure prediction for the same set of sequences, red color indicates alpha-helical regions in ascending intensity according to confidence. Green arrows represent the position of the α helices in the 3D structure of the McpS sensor domain.