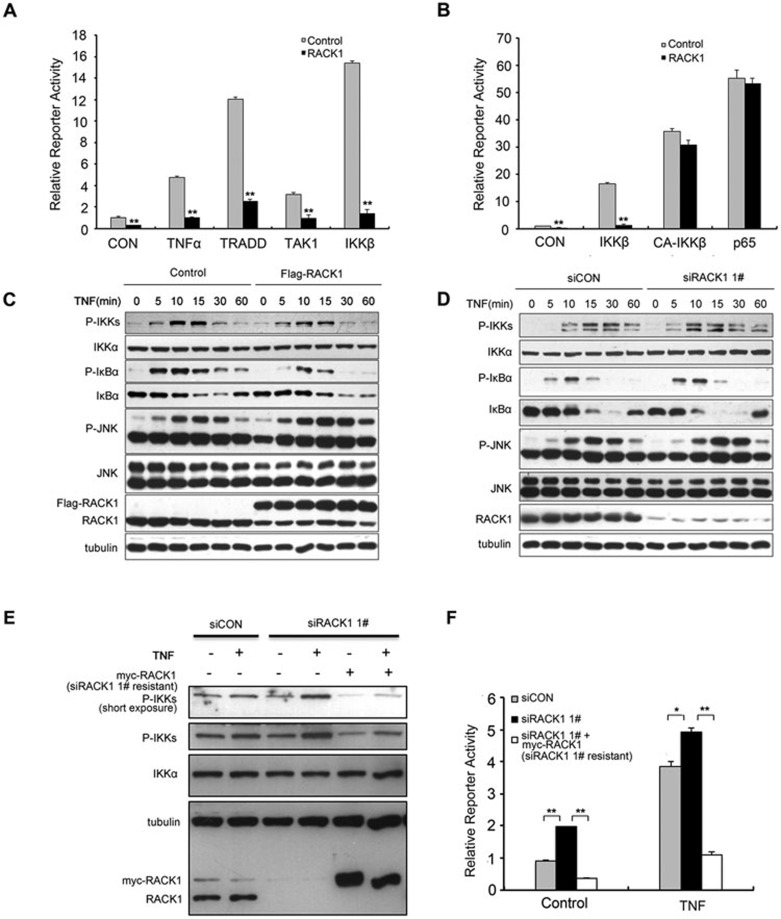
Figure 2.
RACK1 inhibited NF-κB activation by impairing IKK phosphorylation. (A) Overexpression of RACK1 inhibited the NF-κB reporter activity induced by the components of the TNF pathway. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were left untreated or treated with TNF (10 ng/ml) for 6 h before luciferase assays were performed. (B) RACK1 only blocked IKK-dependent NF-κB activation. RACK1 but did not affect the NF-κB activation induced by a constitutively active mutant of IKKβ or p65. CA-IKKβ, constitutively active IKKβ mutant. (C) Overexpression of RACK1 impaired TNF-induced phosphorylation of the IKK complex and delayed degradation of IκBα. 293T cells were infected with Flag-RACK1-expressing or control lentivirus. After puromycin selection, the stable cell lines were treated with TNF (5 ng/ml) before lysis. (D) Knockdown of RACK1 accelerated the TNF-triggered phosphorylation of the IKK complex and degradation of IκBα. (E, F) 293T cells were infected with siRACK1 1# or control siRNA lentivirus and, 48 h later, were transfected with NF-κB-responsive luciferase reporter plasmids and the siRACK1 1#-resistant RACK1 overexpression or control vector. Ninety-six hours after viral infection, the cells were treated with TNF for immunoblotting and luciferase reporter assays. Graphs show the mean ± SD, n = 3. *P< 0.05; **P< 0.01.