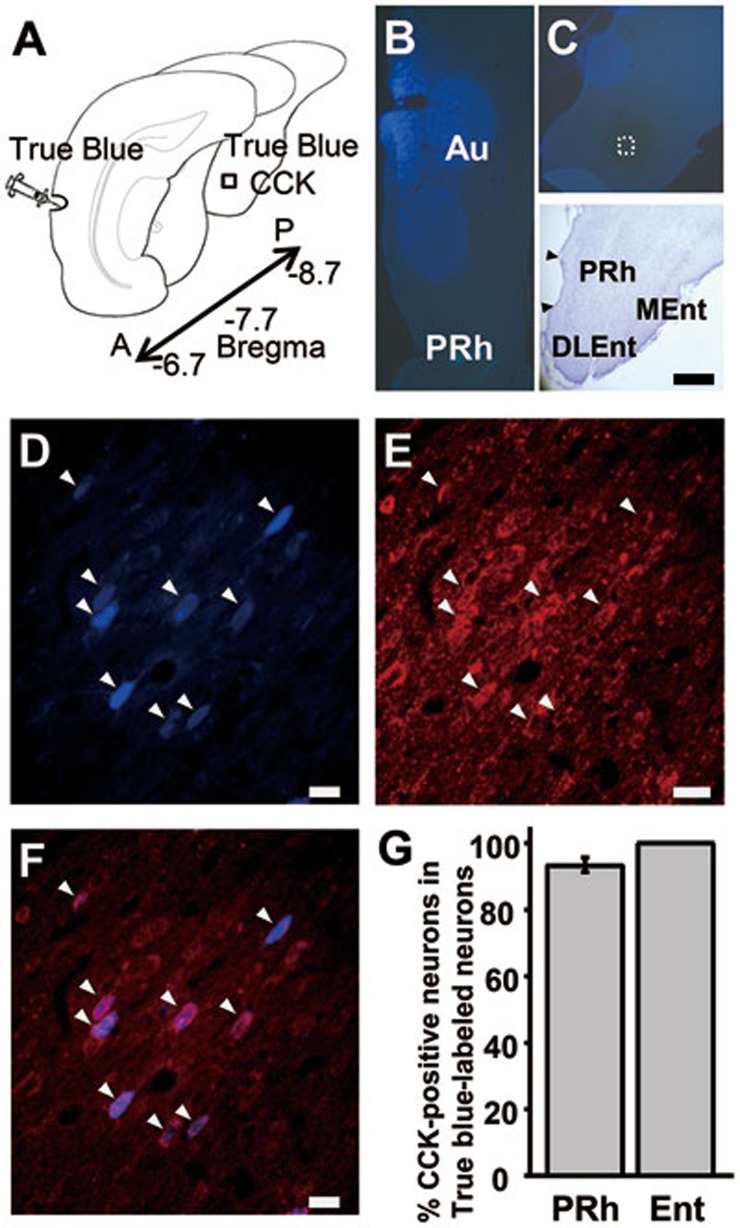
Figure 1.
Perirhinal and entorhinal cortices interact with the auditory cortex through CCK-containing neurons. (A) Experimental preparation. True Blue was infused into the auditory cortex, and True Blue and CCK were co-labeled in the entorhinal cortex. (B) True Blue infusion site in the auditory cortex. (C) Location of the retrogradely labeled neurons in the entorhinal cortex. (D-F) Retrograde True Blue labeling (D) and CCK immunoreactivity (E) in the entorhinal cortex after infusion of True Blue into the auditory cortex. Overlay of the two images (F). (G) Percentage of True Blue-labeled neurons also labeled with CCK in the perirhinal and entorhinal cortices. Nissl stain delineating the boundaries of the hippocampal formation. Au, auditory cortex; PRh, perirhinal cortex; Ent, entorhinal cortex; DLEnt and MEnt, dorsolateral and medial regions of the entorhinal cortex; A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars: 500 μm (A-C); 20 μm (D-F).