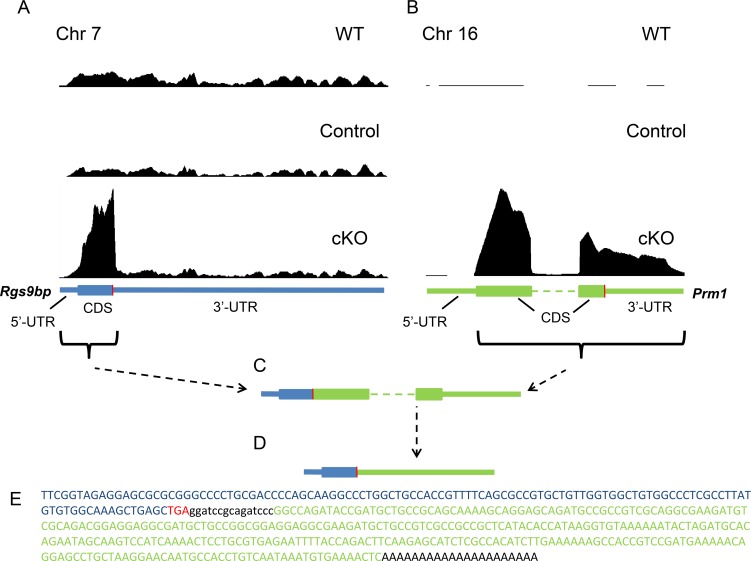
Figure 5.
iCre75-expressing mice also express a Rgs9bp-Prm1 fusion mRNA. (A) Pattern of RNAseq reads mapped to the Rgs9bp gene in WT (C57BL/6J) mice, cKO mice, and control (Dicerfl/fl iCre75−) mouse littermates. The sequence encoding Rgs9bp mRNA is shown below in blue with the translation termination codon indicated in red. The y-axis in (A) and (B) is normalized based on the total number of reads from each sequencing run. (B) Pattern of RNAseq reads mapped to the Prm1 gene in WT (C57BL/6J) mice, cKO mice, and control littermates. The sequence encoding Prm1 mRNA is shown below in green. (C) Schematic representation of the fusion mRNA composed of elements of the Rgs9bp (blue) and Prm1 (green) messages. This fusion mRNA was present in both cKO and iCre75 mouse retinas. Note that this schematic is not drawn to scale as the canonical Rgs9bp transcript (∼6.5 kb) is much larger than the Prm1 transcript (∼500 bp). (D) As the translation termination codon derived from the Rgs9bp mRNA was retained in the fusion transcript, the Prm1 CDS and 3′-UTR together form the 3′-UTR of the fusion mRNA. (E) Sequence of cDNA derived from the 3′-end of the aberrant Rgs9bp transcript in Cre-expressing retinas. Sequences derived from Rgs9bp and Prm1 are shown in blue and green, respectively, with the termination codon shown in red.