Fig. 7.
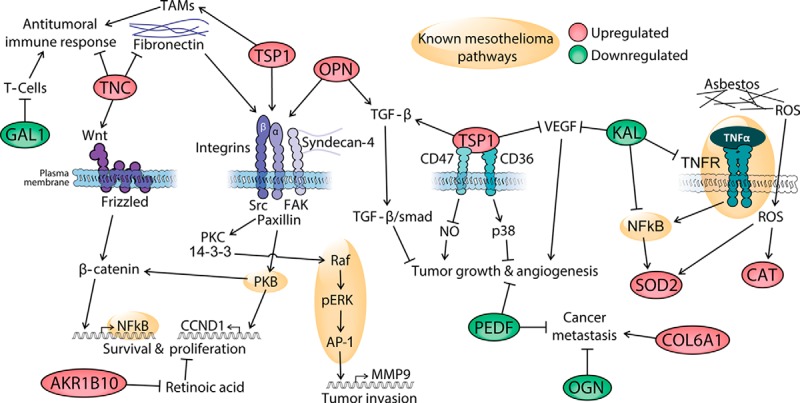
Possible pathophysiological mechanisms underlying mesothelioma. The green- and red-shaded proteins were identified and quantified in this study; red indicates proteins that showed up-regulated levels and green indicates proteins that showed down-regulated levels in pleural effusions from mesothelioma patients, based on MS data. AKR1B10, aldo-keto reductase 1B10; CAT, catalase; COL6A1, collagen, type VI, alpha 1; GAL1, galectin 1; KAL, kallistatin; OGN, osteoglycin; OPN, osteopontin; PEDF, pigment epithelium-derived factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; TNC, tenascin C; TSP1, thrombospondin 1. The links are based on the following literature references: SOD2 and mesothelioma pathways, Ref. 47; KAL, Ref. 51; TNC, TSP, and OPN, Ref. 53; COL6A1, Refs. 55 and 56; OGN, Refs. 57 and 58; PEDF in angiogenesis and metastasis, Refs. 59 and 60; GAL1 and immunosuppression in cancer, Ref. 77; AKR1B10 and proliferation, Ref. 72; OPN and TGF-β, Ref. 78; TSP1 and TAMs, Ref. 79; TSP1, angiogenesis, and tumor growth, Ref. 80.
