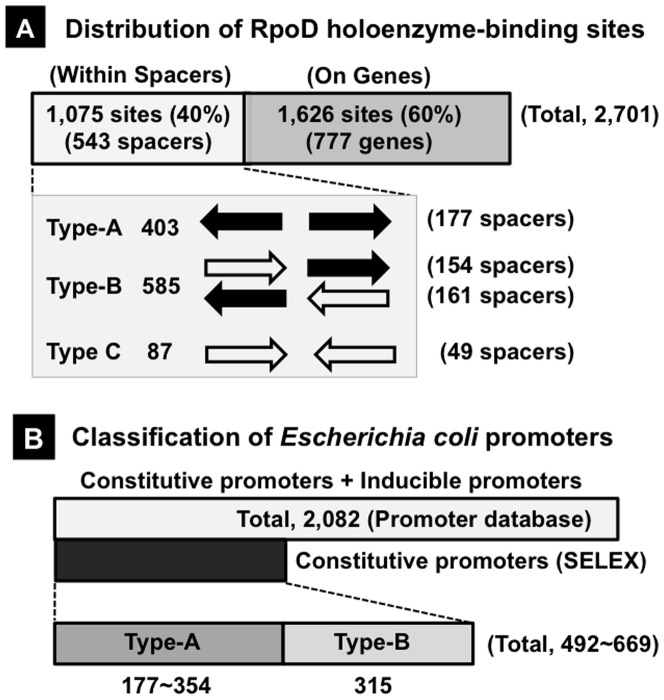
Figure 1. Distribution and classification of the constitutive promoters.
Genomic SELEX search of RpoD holoenzyme-binding sequences was performed using the standard procedure [21]. RpoD holoenzyme-bound DNA fragments were recovered by immunoprecipitation using anti-RpoC antibody. SELEX fragments were isolated from the immuno-precipitates and subjected to mapping on the E. coli genome by using tilling DNA microarray as described previously [32], [33]. [A] Location of the constitutive promoters. A total of 2,701 RpoD holoenzyme-binding sites were identified (see Fig. 1), of which 1,075 (40%) are located within intergenic spacers. On the basis of transcription direction of flanking genes, the spacers were classified into three types: type-A between bidirectional transcription units; type-B upstream of one transcription unit but downstream of another transcription unit; and type-C, downstream of both transcription units. [B] Classification of the constitutive promoters. A total of 2,082 promoters have been identified and listed in the current versions of RegulonDB and EcoCyc databases, whereas the total number of constitutive promoters identified by Genomix SELEX screening ranges between minimum 492 and maximum 669, indicating that the majority of E. coli promoters listed in promoter database are TF-dependent inducible promoters.