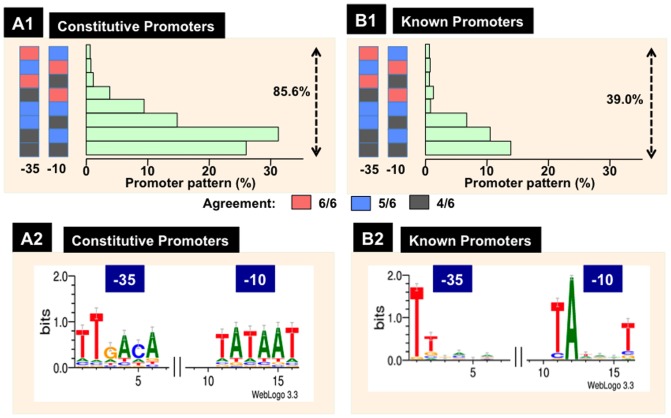
Figure 5. The composition of constitutive promoters.
[A] The known consensus sequences of RpoD-dependent promoter, TTGAAC (-35) and TATAAT (-10) separated by 17 plus/minus 2 bp, were searched for all type-A (177) and type-B (315) spacers (see Experimental Procedure for the analysis method). Most of the constitutive promoters carry high-levels of the consensus sequence as listed in Table 1. The composition of promoter -35 and -10 sequence was classified into 8 groups based on the conservation level of consensus sequences. About 89% of type-A promoters and 82% of type-B promoters (or 86% of A- plus B-type promoters) contain the sequence higher than 4/6 agreement with the consensus sequence at both -35 or -10 positions (A1), while only 39% of a total of 582 known promoters carries this level of consensus sequences (B1). [B] The whole set of constitutive promoter sequences were subjected to Logo analysis [73]. The Logo patterns of -35 and -10 sequences are essentially the same among the constitutive promoters within type-A and type-B spacers. The Logo pattern of the whole set of constitutive promoters was compared with the Logo pattern generated using the total of 582 experimentally identified promoters [19], [20]. The contribution of each base of the consensus -35 and -10 sequences is significantly different between the constitutive promoters and the set of known promoters.