Fig. 5. Celiac artery delivery of AAV9 vector leads to GFP expression in pancreas and several other tissues.
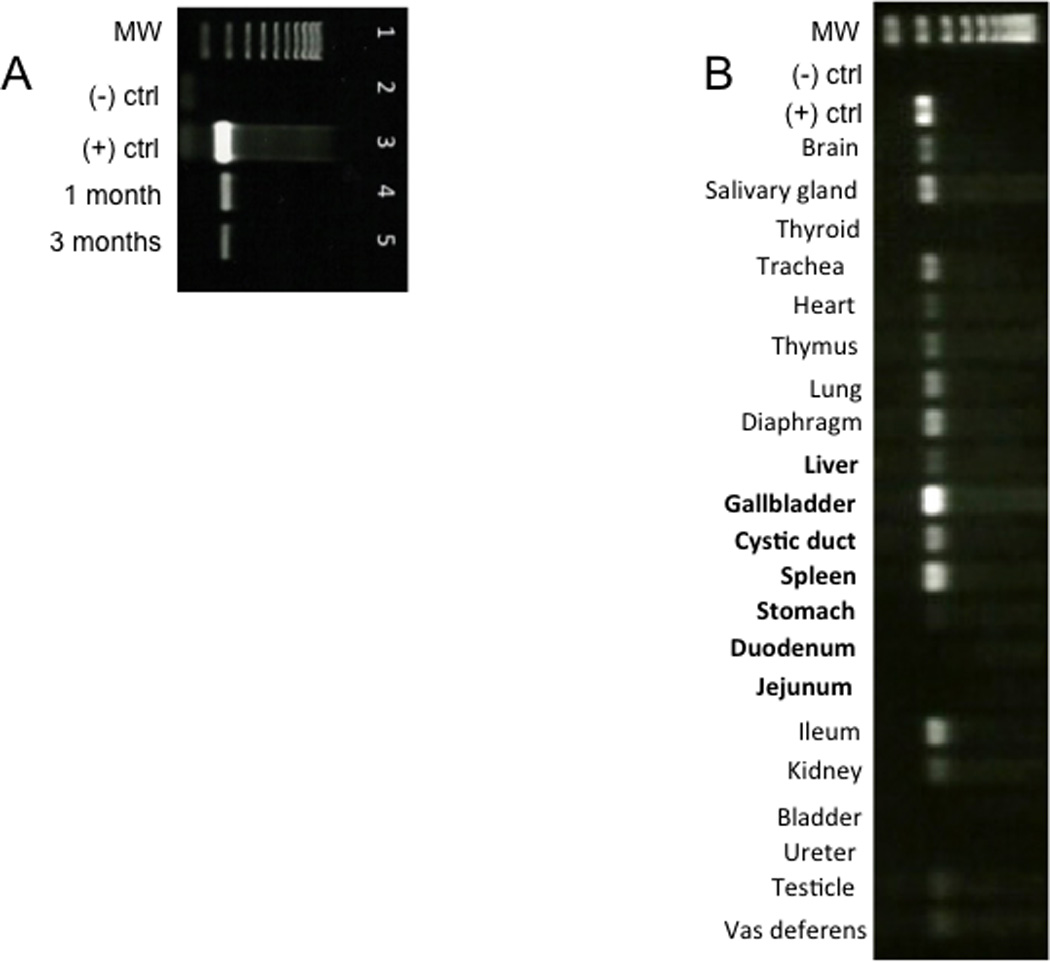
(A) One and three months after delivery of AAV9CMV.sceGFP (2.4×1012 vg per animal) to the celiac artery in the newborn period, RNA was isolated from pancreas and end-point PCR was used to detect GFP mRNA. The results are representative of n=7 for one month exposure and n=1 for three-month exposure. Lane 1=ladder; lane 2=negative control; lane 3=positive control (10 ng GFP plasmid); lane 4=pancreas one month after delivery; lane 5=pancreas three months after delivery. (B). End-point PCR of tissues 30 days after injecting 2.4 × 1012 vg AAV9CMV.sceGFP to the celiac artery of newborn pigs. MW: molecular weight ladder; (−) ctrl: negative control (sham animal); (+) ctrl: positive control (plasmid eGFP). Organs that receive arterial supply from celiac artery are in bold. The stomach and duodenum, two organs that receive blood supply from celiac artery were not transduced.
