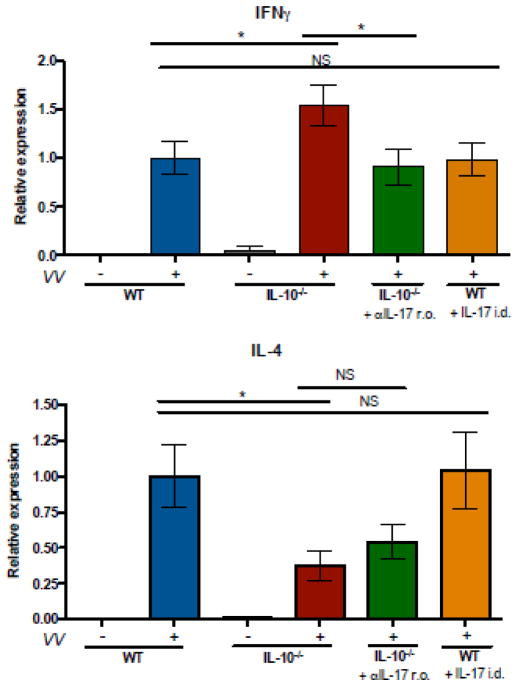
Figure 4. IL-10−/− mice exhibit increased IFN-γ and decreased IL-4 expression in the skin following infection.
IL-10−/− and WT mice were VV-infected via skin scarification with 107 PFU. Anti-IL-17 antibody or isotype control was administered retroorbitally, 3 doses of 100 μg per mouse, on days −1, 0, and 2 relative to infection. IL-17 was injected intradermally, one dose of 2.5 μg per mouse, immediately prior to infection. Transcripts encoding IFN-γ and IL-4 in skin RNA were evaluated by quanititative PCR and normalized to the WT infected group, mean ± SEM, (n=3 for IL-10−/−, uninfected mice; n=5–22 for all other groups). * p < 0.05, by unpaired t test, two-tailed.