Table 2.
Scope of Arylation Using Bromide Substrates
| entry | substrate | product | Conditions A yield[a],[b] | Conditions B yield[c],[d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
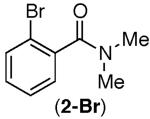
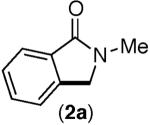
| 1 |
|
|
<10% | <10% |
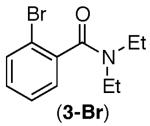
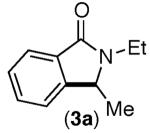
| 2 |
|
|
53% | 47% |
| 3 |
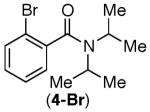
|

|
76% | 89% |
| 4 |
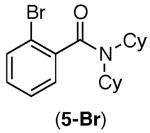
|
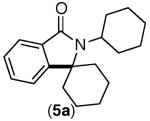
|
92% | 95% |
| 5 |
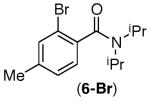
|
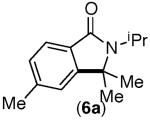
|
83% | 90% |
| 6 |

|
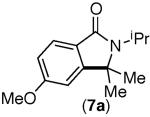
|
80%[d] | trace |
| 7 |
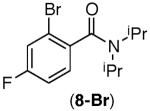
|
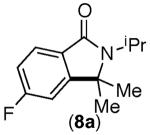
|
60%[d] | 13%[b] |
Conditions A: Ni(COD)2 (0.1 equiv), NaOtBu (1.5 equiv), dioxane, 145 °C.
1H NMR yields against 1,4-dinitrobenzene as the internal standard.
Conditions B: 1,10-phenanthroline (0.2 equiv), NaOtBu (1.5 equiv), dioxane, 145 °C.
Isolated yields (isolated yields were generally within 5% of the crude 1H NMR yields).
