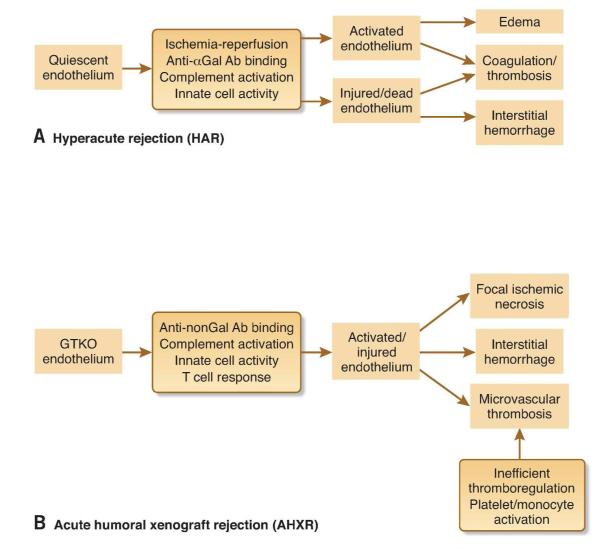
Figure 1. Phases of kidney xenograft rejection.
A, Several factors contribute to hyperacute rejection of wild-type xenografts, but the key events are the binding of preformed anti-αGal antibodies (Ab) to xenograft vascular endothelial cells and subsequent activation of complement. HAR occurs within hours and can be prevented by deletion of αGal (GTKO) or transgenic expression of human complement-regulatory proteins (hCRPs). B, Acute humoral rejection of GTKO xenografts is also mediated by antibodies, in this case anti-non-Gal, but is a more prolonged process (days to weeks) which appears to involve the gradual development of a chronic pro-coagulant and pro-inflammatory vascular environment.