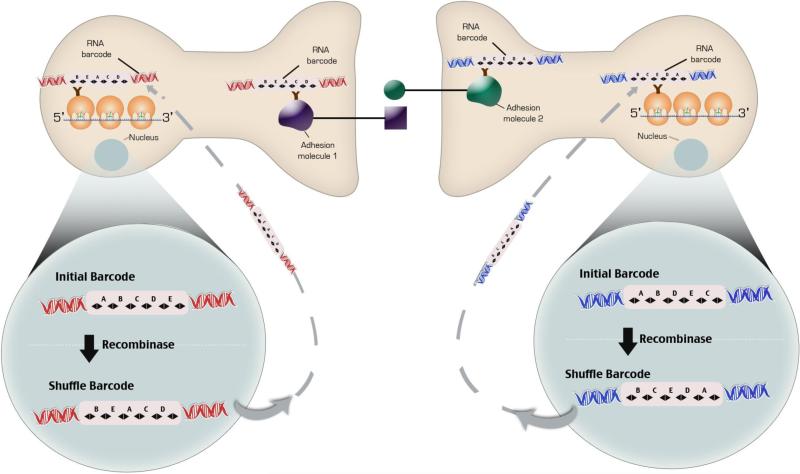
Fig 9.
Schema for correlating cell-type gene expression with connectivity. A Lentiviral vector carrying a unique DNA barcode infects neurons so that each neuron expresses a unique cellular barcode. The DNA element in the viral genome are transcribed and translated such that an RNA barcode is generated. B. In the second schema DNA Barcodes inserted into the Rosa26 locus are placed between loxp sites or another site specific recombinase. Recombination of the barcode sequence is induced by the activation of the recombinase and RNA barcode is generated. The RNA barcode binds to an RNA binding protein inserted in into a ribosomal subunit with EGFP of the cells ribosomes. A RNA binding protein is also inserted into pre- and post-synaptic adhesion molecules that bind to each other. The ribosomes are purified. Complementary DNA sequences attached to a longer DNA sequence are hybridized to the RNA Barcode on the ribosome. PCR primers to the 5' sequence of the complementary DNA sequences attached to a longer DNA and to polyA tail are made such that they join upon the PCR reaction. PCR and sequencing performed. Only mRNAs from that cell will contain the unique barcode sequence. At the same time synaptic adhesion complexes are isolated from synaptomsomes with immunoprecipitation. The DNA barcodes are hybridized to beads containing the complementary sequence and sequenced in a microfluidic chamber.