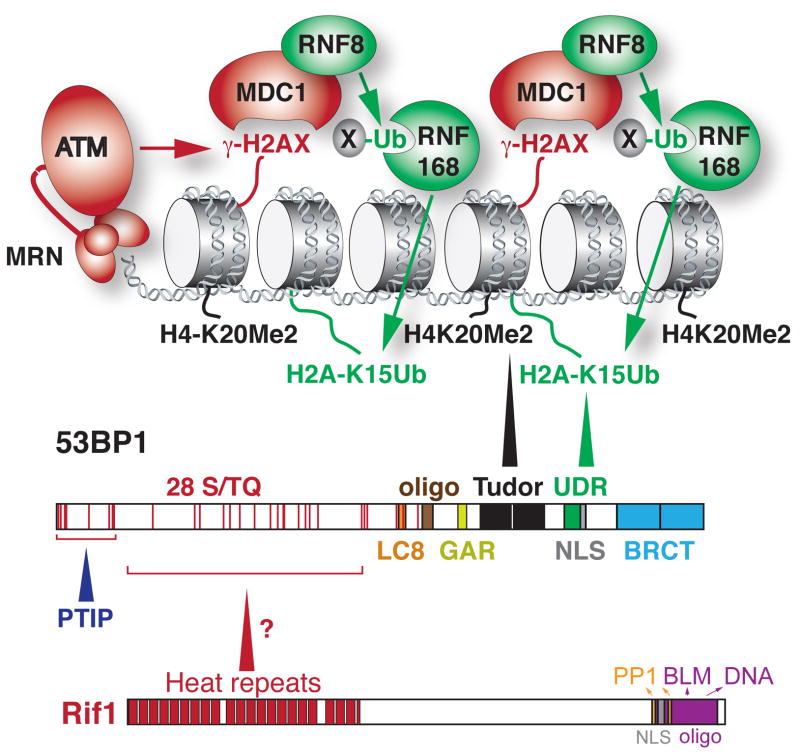
Figure 1.
The domain structures of 53BP1 and Rif1 and the mechanism by which 53BP1 is recruited to DSBs. The binding of 53BP1 requires two histone modifications. The constitutive H4K20Me2 mark (black) is bound by the Tudor domain and the DDR-induced H2A(X)K15Ub marks is bound by the UDR domain. The binding of 53BP1 to damaged chromatin is also promoted by its oligomerization domain. The N-terminal ST/Q phosphorylation sites are important for the interaction of 53BP1 with PTIP and Rif1. See text for details on the mechanism by which the 53BP1 binds to damaged chromatin and Text Box 1 for details on the domain structure of 53BP1. See Text Box 2 for how the spreading of 53BP1 from sites of DNA damage is limited.