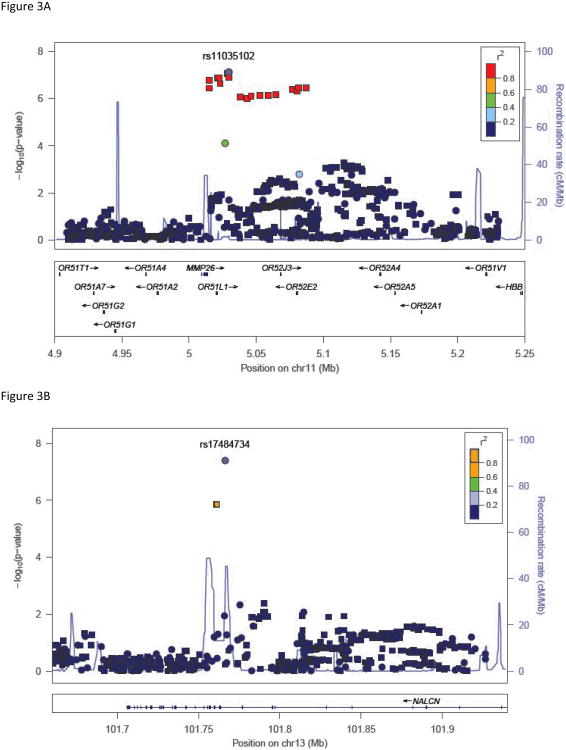
Figure 3. Association results with key phenotypes.
(A) High-risk latent class probability with SNPs in the region around rs17484734 in NALCN. (B) Persistent desire/inability to cut down with SNPs in the region around rs11035201 in OR51L1. Y-axis denotes the –log10(p-value) for association. X-axis is the physical position on the chromosome (Mb). The most significantly associated SNP is shown in purple. The extent of linkage disequilibrium (as measured by r2) between each SNP and the most significantly associated SNP is indicated by the color scale at top right. Larger values of r2 indicate greater linkage disequilibrium. Genotyped SNPs are indicated as circles, and imputed SNPs by squares.