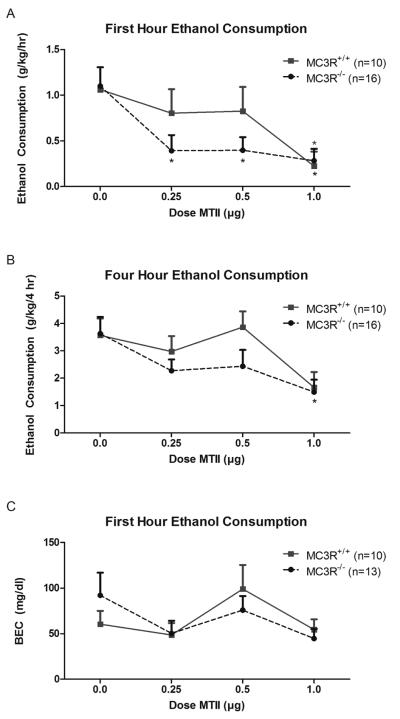
Figure 1.
Ethanol consumed (g/kg) among MC3R−/− and MC3R+/+ mice during the first hour (A), and total four hours (B) of the binge-like ethanol consumption, as well as BEC (mg/dl) measured immediately at the end of the 4-hour test (C). During the first hour, MC3R−/− mice displayed a reduction in binge-like ethanol drinking at all doses tested. Alternatively, significant reductions in drinking were only observed following treatment with the highest dose (1.0 μg) of MTII in MC3+/+ mice. Similarly, at the end of the 4-hour test, only the highest dose of MTII caused a reduction in binge-like ethanol drinking in MC3R−/− mice. No significant effect of MTII was observed on BEC regardless of genotype. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * signifies p < .05 relative to vehicle within that genotype.