Fig. 3.
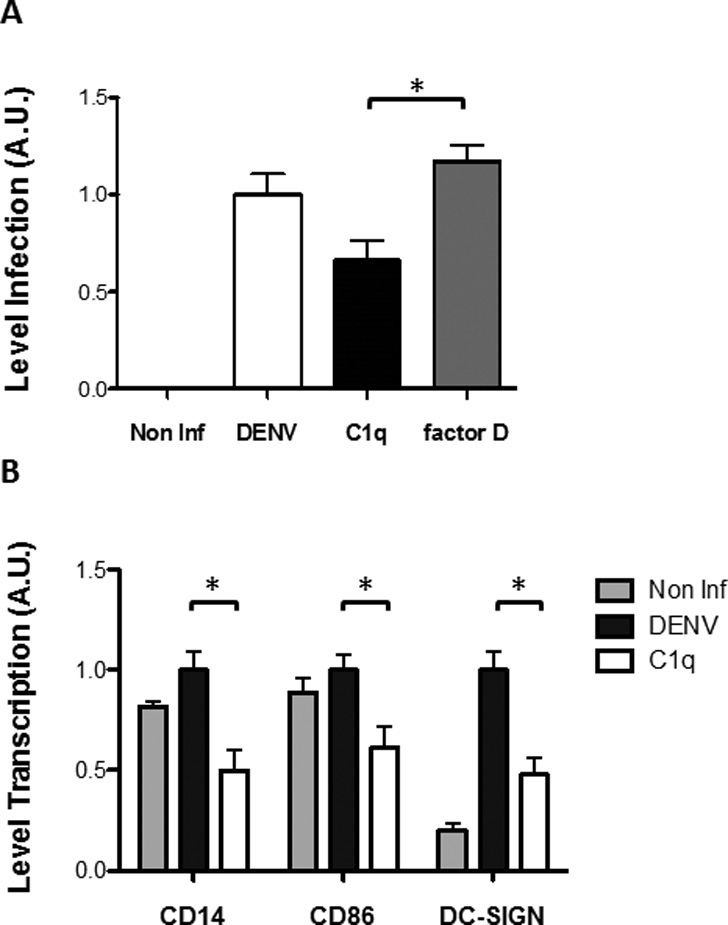
Incubation of DENV2 with C1q leads to a decrease in infection and in the levels of transcription of cellular factors. (A) DENV2 strain 16681 viruses were incubated either with vehicle (DENV), C1q and factor D at 37°C for 1 hour prior to infection of THP-1 cells and the level of infection was measured by RT-PCR 24 hours later. Cells infected with DENV2 incubated with C1q, but not with factor D, had a significant decrease in infection of around 30%. DENV2 viruses were incubated with the complement molecules in their physiological concentration, i.e., the concentrations they are normally found in human blood, 10 µg/ml and 750 ng/ml for C1q and factor D, respectively (Nascimento et al., 2009b). (B) Levels of transcription of several cellular factors are altered by infection of THP-1 with DENV2 previously incubated with C1q. DENV2 strain 16681 viruses were incubated either with vehicle (DENV) or C1q at 37°C for 1 hour prior to infection of THP-1 cells and the level of transcription of several proteins involved in viral clearance was measured by RT-PCR 24 hours later. Levels of CD14 (involved in monocyte maturation), CD86 (involved in the induction of a T cell response) and DC-SIGN (a cellular receptor involved both in viral infection and modulation of innate immune response) show, are significantly decreased in cells infected with virus pre-incubated with C1q. Results obtained are representative of 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was done using GraphPad program and Student’s paired, 2 tails t-test. Values were considered significant when p<0.05.
