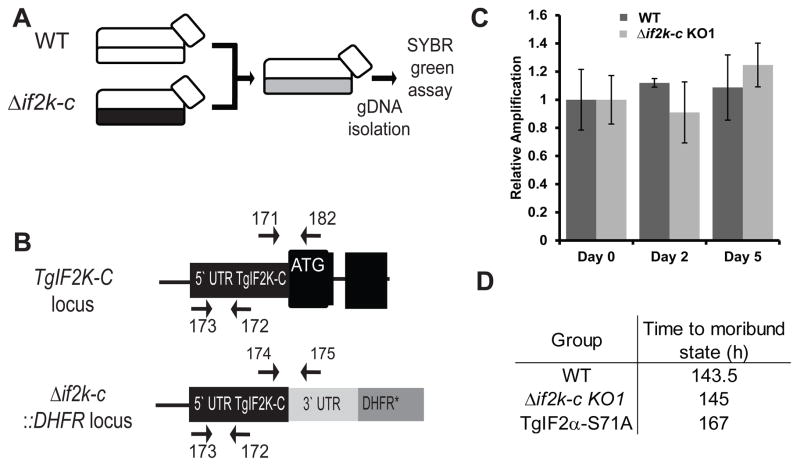
Fig. 4.
Toxoplasma gondii (Tg)IF2K-C is dispensable for normal progression through the lytic cycle. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental set up for the competitive fitness assay. Equal numbers of parental wild-type (WT) and Δif2k-c parasites were co-cultured in the same flask. Genomic (g)DNA from the mixed population was isolated for SYBR-green PCR analysis at days 0, 2 and 5. (B) Diagram of genomic loci and oligonucleotides that were used to distinguish WT and Δif2k-c parasites. (C) Relative levels of parasite genomic DNA in the co-cultured flasks were determined using a SYBR-green assay and oligonucleotide primers #171 and #182 or oligonucleotides #174 and #175, which are specific for WT or Δif2k-c parasites, respectively. A fragment of the 5′-untranslated region (UTR) conserved between WT and Δif2k-c parasites was amplified with the oligonucleotides #173 and #172 to normalize the samples. The results of Δif2k-c clone KO1 are shown. Error bars indicate the S.D. from a triplicate experiment. Analysis of the Δif2k-c clone KO2 showed a similar result. (D) BALB/c mice were infected i.p. with 100 WT, Δif2k-c or TgIF2α-S71A parasites. The average time to a moribund state was determined for each group of infected mice.