Figure 6. ProSAAS prevents Aβ1-42 -induced cytotoxicity in Neuro2a cells.
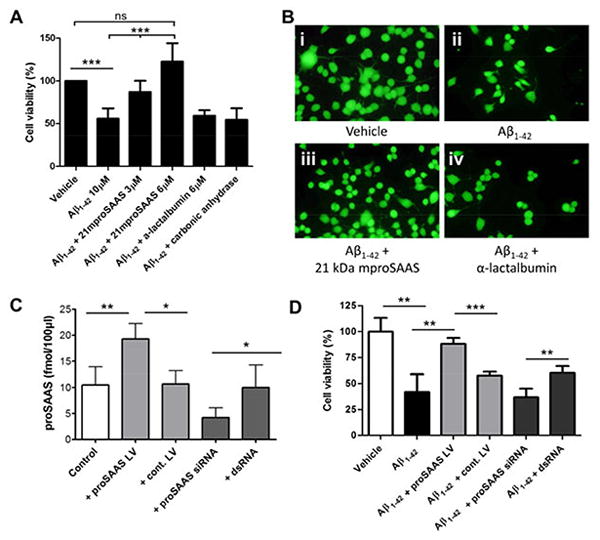
A. Neuro2a cells were incubated for 48 h with a 10 μM Aβ1-42 oligomer mixture, which resulted in about 50% cytotoxicity. The addition of 21 kDa mproSAAS to the medium during the 48 h treatment significantly prevented Aβ1-42-mediated cell death in a dose-dependent manner, as assessed by WST-1 viability assay. α-lactalbumin (6 μM) and carbonic anhydrase (6 μM) were added as negative controls in parallel sets of Aβ1-42-treated Neuro2a cells. Results represent the mean ± SD, N=4. B. Representative images of Neuro2a cells treated with vehicle (i), Aβ1-42 (ii), Aβ1-42 + 21 kDa proSAAS (3 μM) (iii), and Aβ1-42 + α-lactalbumin (3 μM) (iv), stained with calcein AM. C. In order to validate the proSAAS siRNA and lentivirus, endogenous proSAAS levels in a 6-well plate of Neuro2a cells were measured by radioimmunoassay after treatment with either proSAAS-encoding lentivirus, no lentivirus, proSAAS siRNA, or control dsRNA. Control lentivirus and control dsRNA had no effect on the endogenous level of proSAAS. D. Lentiviral-mediated overexpression of proSAAS rescued Neuro2a cells from Aβ1-42-induced cytotoxicity, as measured in the 96-well plate cytotoxicity assay. siRNA mediated knockdown of proSAAS resulted in reduced cell viability compared to Neuro2a cells treated with Aβ1-42 and a control dsRNA. One-way ANOVA or t-test was used to determine statistical significance. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01, and *** = p<0.001.
