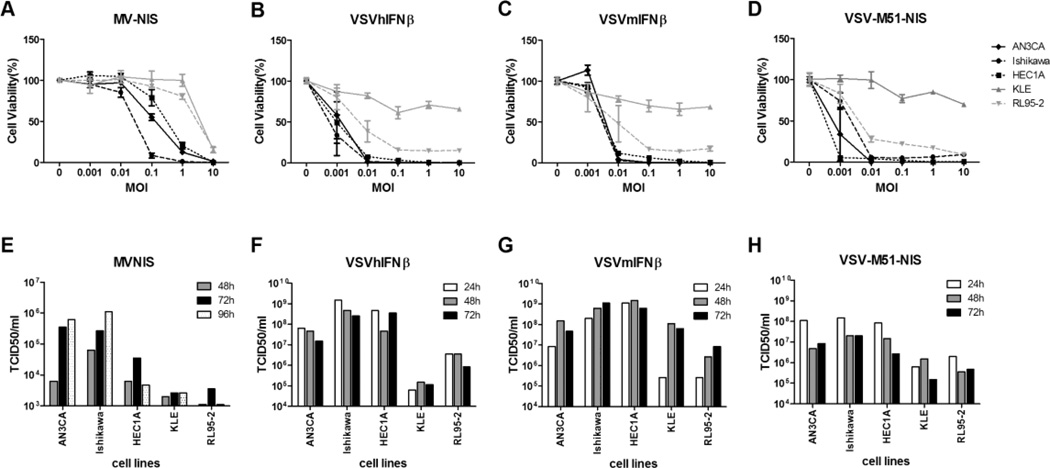
Figure 1.
Cell-killing ability and progeny propagation of MV and VSV variants in type I EC cell lines. A, B, C, and D, AN3CA, Ishikawa, HEC1A, KLE, and RL95-2 cell lines were evaluated for MV-NIS–, VSV-hIFNβ-, VSV-mIFNβ-, and VSV-M51-NIS–induced cytotoxicity as determined by the MTS cell viability assay. Cells were infected with viruses at the indicated MOI. MTS assays were performed 48 hours after VSV infections and 120 hours after MV infection. E, F, G, and H, Cells were treated with MV-NIS, VSV-hIFNβ, VSV-mIFNβ, and VSV-M51-NIS under multiple-cycle (MOI 0.02) infection conditions. At various times after infection, cells or small aliquots of supernatant were collected, and the amount of viral progeny was determined by TCID50 assay. Abbreviations are defined in the text.