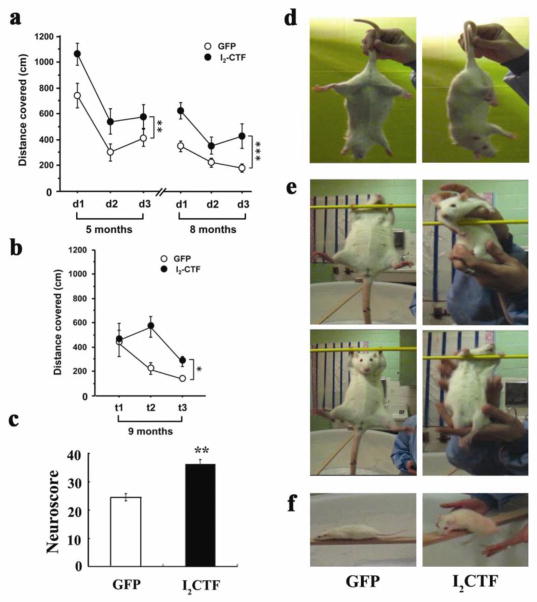
Fig. 3. I2CTF expression induces spatial reference memory and neurological and motor impairments.
a. Compared to GFP control (n=7), I2CTF (n=8) rats showed impairment in spatial reference memory at 5 (p=0.005) and at 8 (p<0.001) months of age in Morris Water Maze task and b. in long-term spatial reference memory examined one month later (at 9 months of age) by transfer task in the water maze (p=0.041). d=day; t=trial; asterisks refer to statistical difference between the two curves and not any single time point; *p<0.05; **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001. c: I2CTF rats (n=8) presented a higher neuroscore than GFP rats (n=7), reflecting a robust neurological impairment; d: I2CTF rats displayed severe muscle atrophy, inducing abnormal posture and hind limb clasping; e: weakness in prehensile strength; and f: disability in walking.