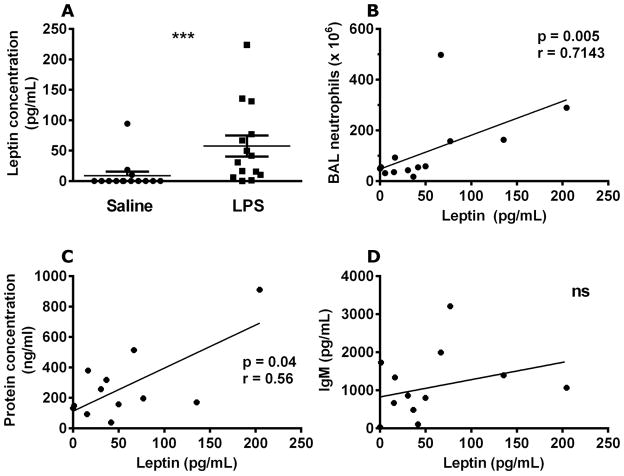
Figure 2.
Airspace leptin levels are increased by LPS exposure in humans. Human leptin was quantified in brochoalveolar lavage fluid from lung segments exposed to either saline (10mL) or LPS (4ng/kg in 10mL saline) 16 h after instillation (A). The increase in leptin expression was compared to the levels of brochoalveolar lavage neutrophils (B), total brochoalveolar lavage protein concentration (C), and IgM levels (D). n=14 in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, * p≤0.05 compared to control. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to analyze differences between paired LPS and saline instilled subsegments from each subject (A), and Spearman rank correlation was used to analyze the relationship between LPS-treated subsegment lavage leptin, neutrophil, protein, and IgM levels, which were adjusted for the matched control subsegment in each subject (LPS-instilled subgement minus saline instilled subsegment).