Figure 2. Intermolecular interactions between ACP and LpxD.
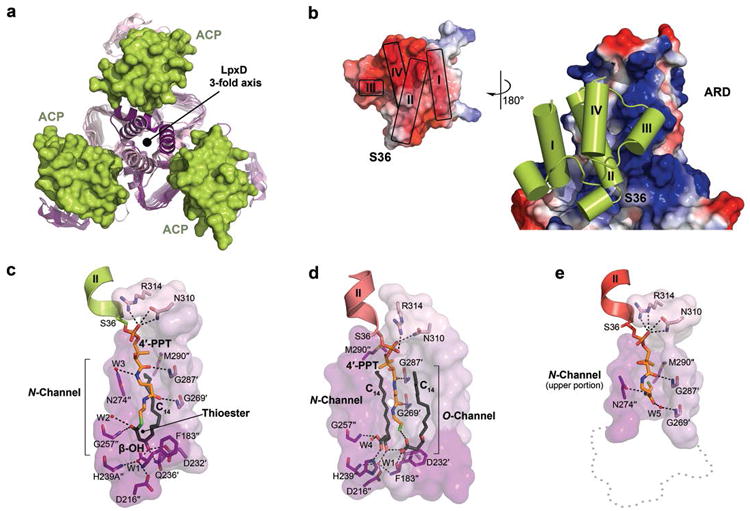
(a, b) Overview of the protein-protein interactions (intact-acyl-ACP depicted). (a) Top-down view of the ACP-LpxD complex showing three molecules of ACP bind per LpxD trimer. (b) Electrostatic surface representation of the ARD and ACP (inset), the potential contours were scaled to +79.2 (blue) and -79.2 (red) KbT e-1. (c, d, e) Detailed interactions between the LpxD reaction chamber and the bound acyl/4′-PPT groups of ACP. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashes. Molecular surfaces are of only those residues that contribute to interactions. (c)Intact-acyl-ACP complex. The β-OH-C14 acyl-chain delivered by ACP binds the hydrophobic N-channel and its terminal carbon-atoms pack near Met290″. (d)Hydrolyzed-acyl-ACP complex. An equivalent β-OH-C14 acyl-chain is shown bound to a newly identified hydrophobic channel (O-channel). (e)Holo-ACP complex. The 4′-PPT arm interacts at the far end of the N-channel, positioning the terminal thiol near Met290″. A ‘ghost outline’ of the catalytic cleft is indicated by a gray dotted line.
