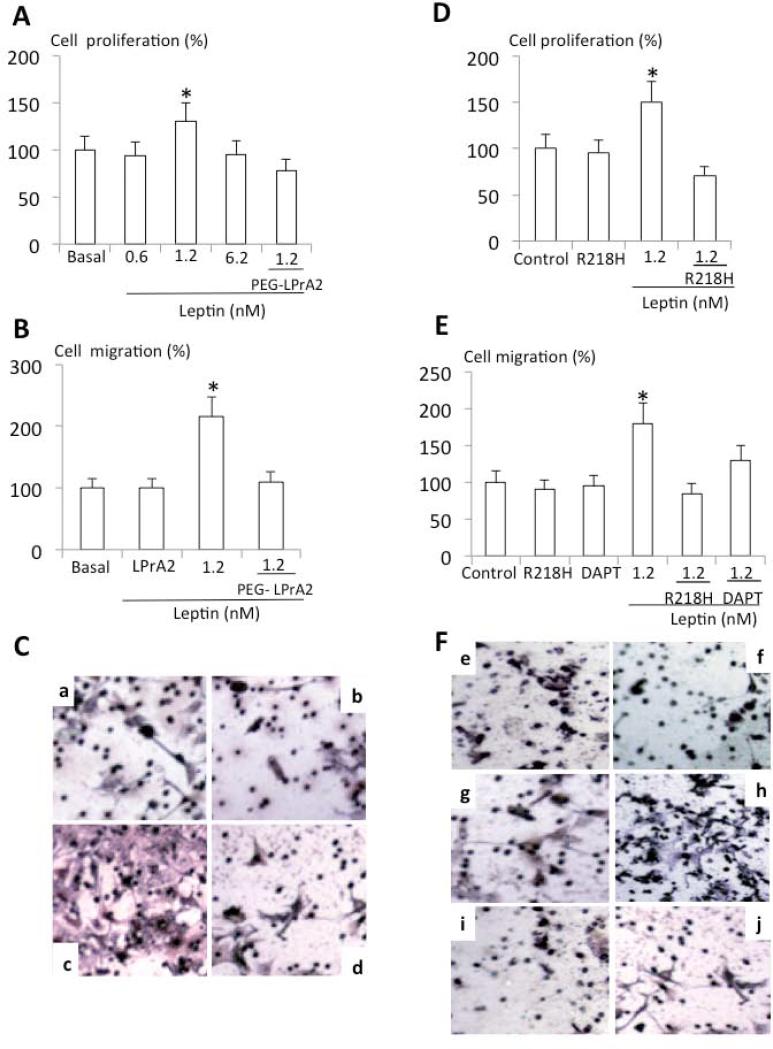
Fig 2. Notch's loss-of–function completely inhibits leptin-induced proliferation and migration of E0771 cells.
Leptin-dose response effects on proliferation (A) and migration of E0771 wild type cells (B). Representative results of leptin and PEG-LPrA2 effects on migration of E0771 wild type cells (C). Detection of migration of E0771 wild type cells: basal (Ca); PEG-LPrA2 treated (Cb); leptin-treated (Cc) and leptin+PEG-LPrA2 treated (Cd). Leptin effects on proliferation (D) and migration (E) of E0771-R218H as compared to control E0771 wild type cells. Representative staining of migration of E0771 wild type and R218H expressing cells (F). Detection of migration: basal E0771 wild type cells (Fe); basal E0771-R218H cells (Ff); E0771 wild type cells treated with DAPT (Fg); E0771 wild type cells treated with leptin (Fh); E077-R218H cells treated with leptin+ DAPT (Fi) and E0771 wild type cells treated with leptin+ DAPT (Fj). Proliferation (MTT) and migration (Boyden chamber) assays were carried-out after 24h of incubation in different conditions and results were normalized to basal conditions (see Material and Methods). P<0.05 when comparing cell migration and proliferation to control (basal). Data (mean ± standard error) representative results derived from a minimum of 3 independent experiments. PEG-LPrA2: pegylated leptin receptor antagonist 2; R218H: dominant-negative RPB-Jk (CSL) plasmid; DAPT: [N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester], a γ-secretase inhibitor.