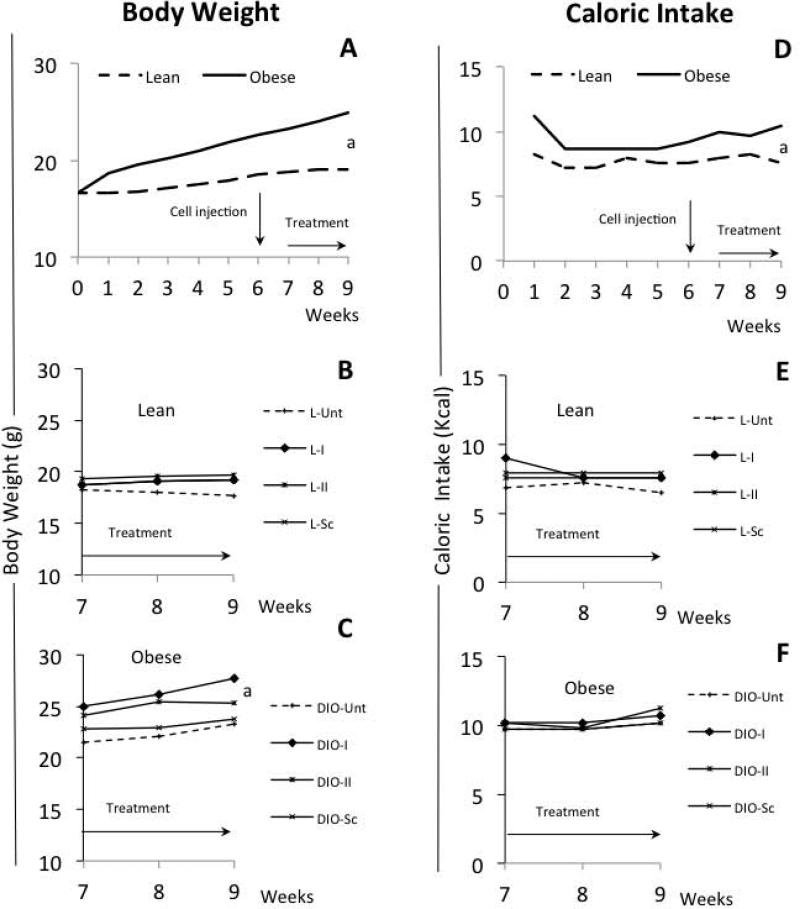
Fig 3. Effects of diets and PEG-LPrA2 treatment on body weight (BW) and caloric intake.
Weekly evaluation of BW of mice fed chow (lean; n=20 mice; normal diet 10% Kcal-fat) and high-fat diets (DIO, diet-induced-obesity mice; n=30 mice, 60% Kcal-fat) (A). Impact of PEG-LPrA2 treatment on BW of lean (B; n=20) and DIO-mice (C; n=22) mice after E0771 cell inoculation. Effects of consuming chow and high-fat diets on caloric intake of lean and DIO-mice (D). Caloric intake overtime of lean (E) and DIO-mice (F) after PEG-LPrA2 treatment. Obesity in DIO-mice (73%; 22/30) was evaluated at week 5 (see M&M). Mice were orthotopically inoculated with E0771 cells (1×105 cells). At week 6, lean and DIO-mice were allocated to 4 subgroups each. Mice were untreated (L-Unt; n=5 and DIO-Unt; n=7) or received inactive peptide (L-Sc; n=5 and DIO-Sc; n=5) or PEG-LPrA2 treatment [once (L-I; n=5 and DIO-I; n=5) or two times (L-II; n=5 and DIO-II; n=5) a week for 3 weeks]. (a) P<0.05 when comparing BW or caloric intake between lean and DIO mice. PEG-LPrA2: pegylated leptin receptor antagonist 2.