Figure 3. Peptide residues lie in distinct CALP binding sites.
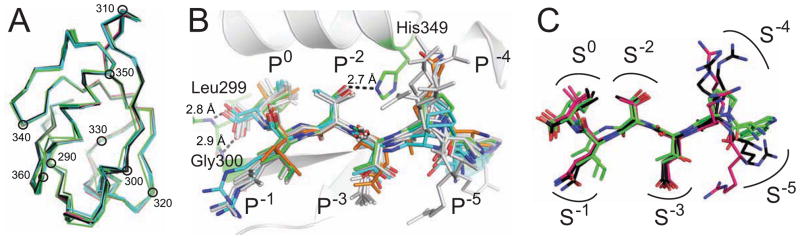
(A) Cα traces are shown for CALP protomers from each of four different space-groups (Table S1), following superposition of main-chain atoms on the B-protomer of CALP:iCAL36. Traces are colored by space group: P212121 (black), P1 (green), P21 (cyan), and P6322 (pink). Every 10th residue is indicated with a black circle and residue number. The tight clustering reveals no gross conformational changes in the PDZ domain based on lattice packing, peptide sequence, or affinity. See also Figure S3.
(B) Following superposition of PDZ main-chain atoms, chimeric iCAL36/CFTR peptides (stick figures) bind CALP (cartoon, gray) in similar conformations, despite sequence and affinity differences (Table 1). Characteristic PDZ hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines, including carboxylate interactions with residues Gly300 and Leu299 and a P−2 interaction with His349 (stick figures). iCAL36 (green carbons) and the highest (iCAL36TRL; cyan) and lowest (iCAL36VQD-3; orange) affinity peptides are highlighted for reference. Other peptides (gray) include iCAL36QDTRL, iCAL36Q-4, iCAL36L, HPV16 E6, and HPV18 E6. See also Figure S8A–G.
(C) Following superposition of PDZ main-chain atoms, bound peptide conformations are shown for C-terminal peptides derived from the HPV16 (black) and HPV18 (pink) E6 proteins together with iCAL36 (green). Binding sites are shown schematically for each position (S0, S−1, etc.). Non-carbon atoms are colored by element (red = O, blue = N)
