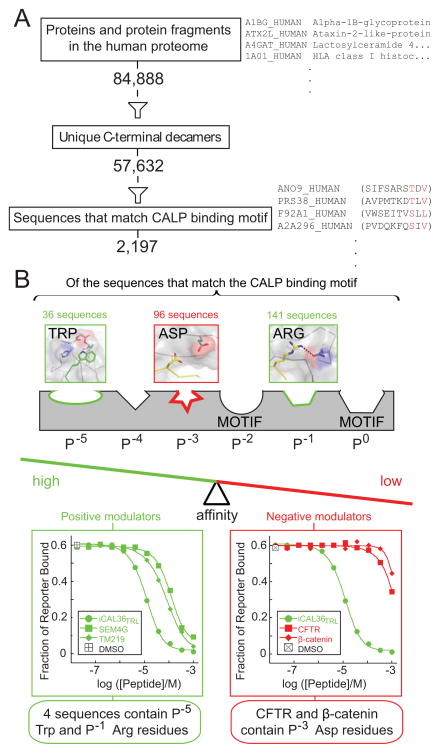
Figure 6. Impact of binding motif and modulator residues on PDZ binding specificity.
(A) Evaluation of the number of unique C-terminal decamers in the human proteome that satisfy the CALP binding motif (red residues in example sequences listed at right).
(B) A schematic pharmacophore model of the series of side chain-binding sites along the CAL PDZ cleft is shown, some of which are identified as binding motif residues by high-throughput analysis (Figure 1A). Positive (green) and negative (red) preferences are shown at non-motif sites, together with the frequencies of these residues in the pool of potential CALP binders. FP displacement titrations confirm the expected affinities for representative peptides that contain positive (left panel, green) and negative (right, red) modulator residues, suggesting that modulators can significantly restrict the number of binding partners by adjusting the overall affinity balance of the PDZ:target interaction. See also Figure S8H.