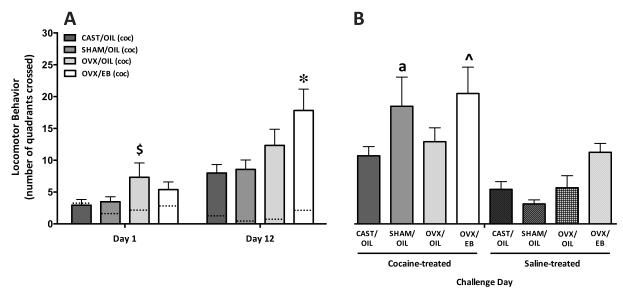
Figure 2. The effect of hormones on and sex differences in locomotor behavior (quadrant crossings) after 10 mg/kg cocaine.
A) The mean number of quadrants crossed (+/−SEM) in 60 min on Day 1 and Day 12 of treatment. (The dashed lines within the bars represent the means for the saline-treated groups.) On Day 1, OVX/OIL females exhibited higher locomotor activity compared to CAST/OIL and SHAM/OIL males ($ p < 0.05). Sensitization (stereotyped behaviors on Day 12 minus Day 1) was seen in all cocaine-treated groups. The OVX/EB females show a greater increase in locomotor behavior than the other three groups (* p < 0.05). B) The number of quadrants crossed after a challenge dose of cocaine by animals receiving cocaine (left side; solid bars) or saline treatment (right side; notched bars) for the first 12 days. On Challenge Day only the SHAM/OIL males previously treated with cocaine exhibited sensitization relative to saline-treated counterparts (a, p < 0.05). Within the animals previously treated with cocaine, OVX/EB females showed the greatest increase in locomotion compared to the CAST group (^ p < 0.05). There were no differences in Challenge Day locomotion among the saline-treated groups.