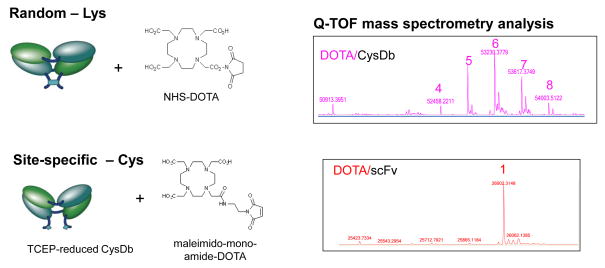
Figure 4.
Random vs. site-specific conjugation of a chelating agent to an ALCAM-specific cys-diabody. Conjugation to random lysine residues was accomplished using NHS-DOTA; site-specific conjugation was conducted by mild reduction using TCEP followed by reaction with maleimido-DOTA. On the right, mass spectrometry analysis reveals a range of modification (4–8) by the random method, and uniform addition of a single DOTA moiety to each monomer chain of the cys-diabody following site-specific conjugation (K. McCabe, R. Moore., T. Lee, unpublished).