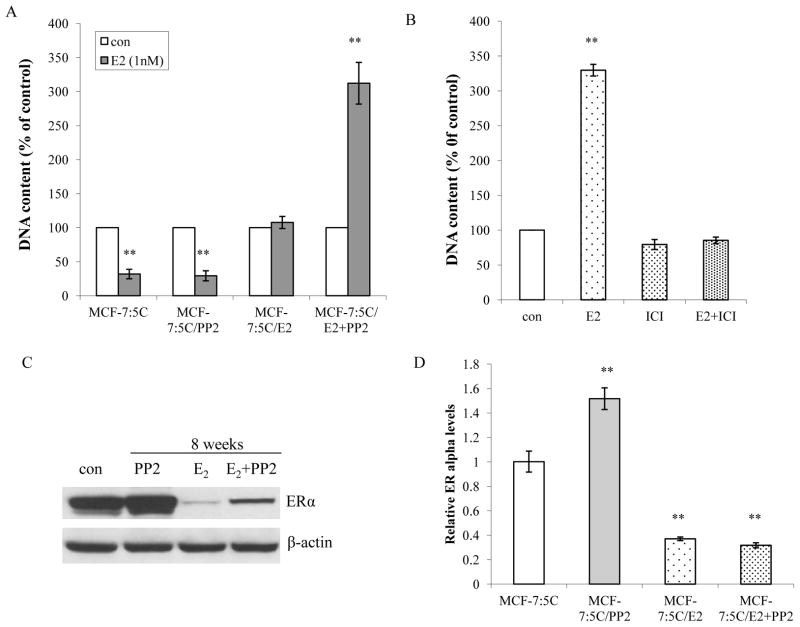
Figure 2. The c-Src inhibitor converted E2 responses from inducing apoptosis to stimulating growth.
(A) Responses to E2 in treated cells. Cells treated in different combinations were seeded in 24-well plates in triplicate. Cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% EtOH) or E2 (10−9mol/L) without any other compounds in the medium. The cells were harvested after 7 days treatment and total DNA was determined using a DNA fluorescence quantitation kit. P<0.001, ** compared with control. (B) E2 proliferative effect was blocked by ICI182,780. MCF-7:PF cells were seeded in 24-well plates in triplicate. After one day, the cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% EtOH), E2 (10−9mol/L), ICI 182,780 (10−6mol/L), and E2 (10−9mol/L) plus ICI182,780 (10−6mol/L) respectively. The cells were harvested and total DNA was determined as above. P<0.001, ** compared with control. (C) Changes of ERα after long-term treatment. Cell lysates of different long-term treated cells were harvested. ERα was examined by immunoblotting. β-actin was detected for loading control. (D) Changes of ERα mRNA levels. The RNA of different cells was harvested in TRIzol for real-time PCR analysis. All the data shown were representative of at least three separate experiments with similar results.