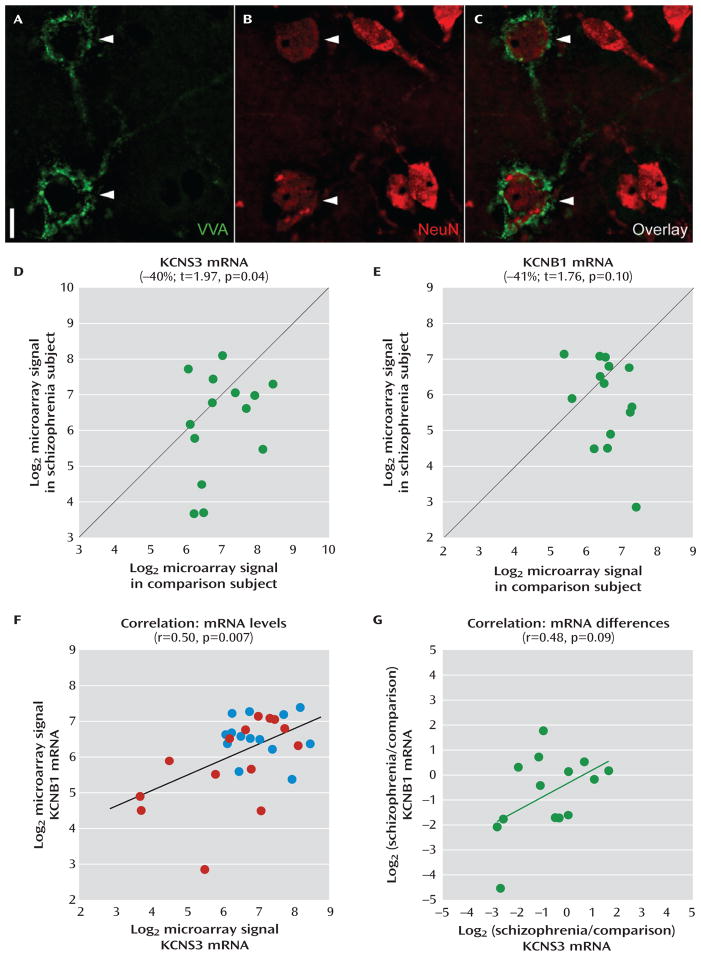
FIGURE 3. Microarray Analysis of KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNA Levels inVicia villosa Agglutinin (VVA)-Labeled Neurons in Schizophrenia and Comparison Subjectsa.
a Representative photomicrographs demonstrate dual-fluorescence labeling using biotinylated VVA to detect perineuronal nets (panel A) and an antibody against the neuronal protein NeuN (panel B). In panel C, an overlay of panels A and B illustrates that only some neurons (arrowheads) are surrounded by perineuronal nets. Scale bar=10 μm. Log2-transformed microarray signals of KCNS3 (panel D) and KCNB1 (panel E) mRNAs for schizophrenia subjects relative to matched comparison subjects are plotted for each pair. Green circles represent each subject pair. Data points to the right of the unity line indicate lower mRNA signals in the schizophrenia subject relative to the comparison subject and vice versa. Mean KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNA levels were decreased by 40% and 41%, respectively, in schizophrenia subjects relative to matched comparison subjects. In panel F, log2-transformed microarray signals for KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNAs are plotted across 28 subjects, with blue and red circles representing comparison and schizophrenia subjects, respectively. Pearson’s correlation analysis revealed a significant correlation between KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNA levels. In panel G, log2-tranformed signal ratios between schizophrenia and comparison subjects were calculated for both KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNAs in each pair and plotted across 14 pairs. Green circles represent each subject pair. Pearson’s correlation analysis detected a trend toward correlated reductions of KCNS3 and KCNB1 mRNAs in schizophrenia.