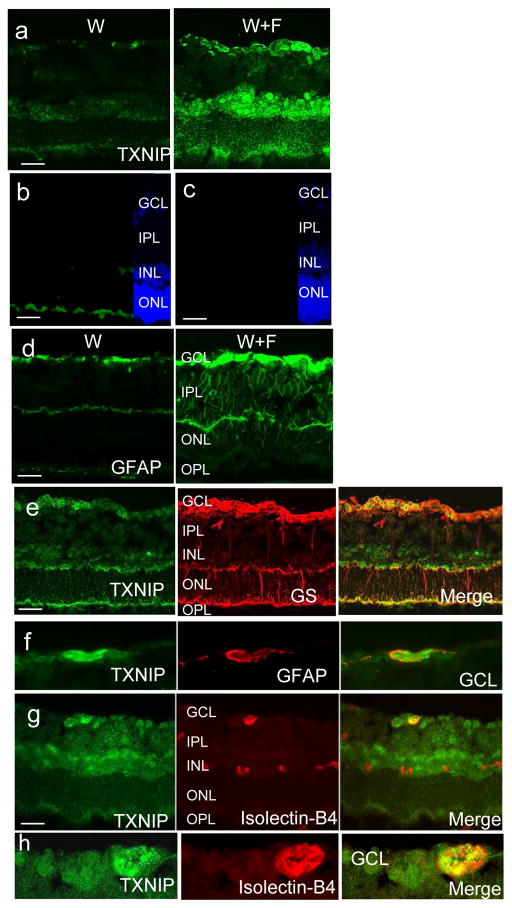
Fig. 5.
HFD-induced TXNIP expression co-localises within retinal vasculature and glial cells. (a) Increased TXNIP expression was observed in the GCL, INL and, to a lesser extent, ONL in the W+F group relative to the control W group. (b, c) Negative controls (b, normal rabbit serum; c, no primary antibody) showed specific binding for TXNIP antibody in the GCL and INL but not in the ONL. (d) HFD induced GFAP activation in the W+F group. Co-localisation of TXNIP with glutamine synthase (GS) (e), GFAP (f) and isolectin-B4 (g) staining showed strong association in the GCL, suggesting astrocytes, Müller cell endfeet and retinal microvasculature in GCL (enlarged in h), as well as deep retinal capillaries in the INL. Magnification, ×200, scale bars, 25 μm