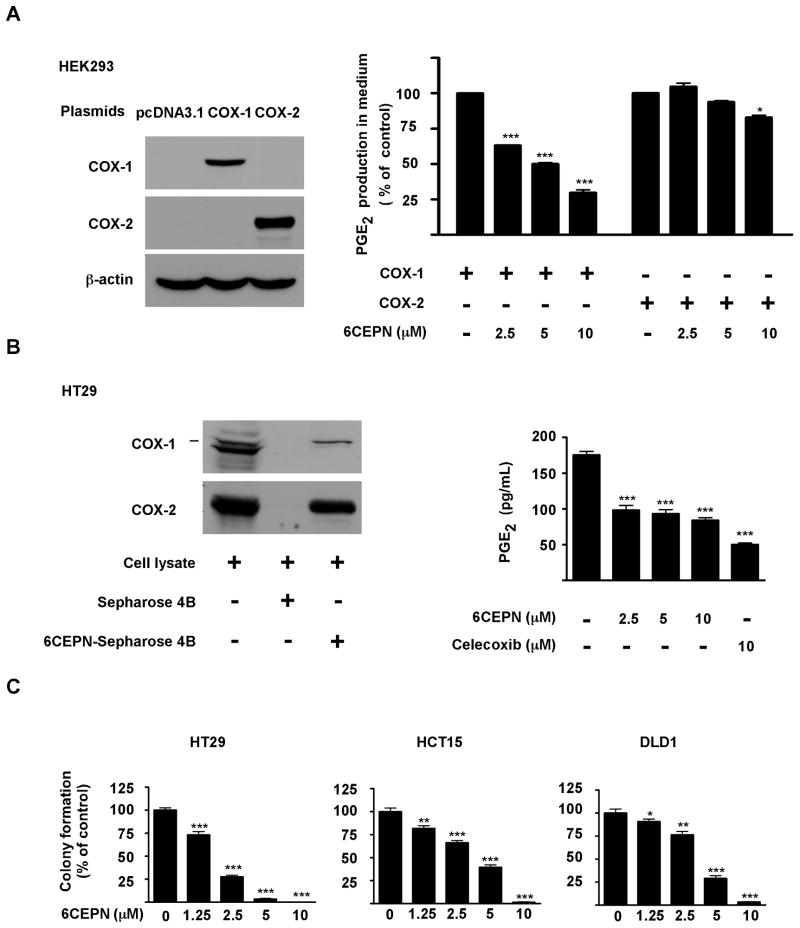
Figure 4.
6CEPN targets COX-1 ex vivo. A, 6CEPN specifically inhibits COX-1 activity in HEK293T cells. The effector plasmids (COX-1 and COX-2) and control plasmid (pcDNA3.1) were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells using jetPEI reagent (Qbiogen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. After 24 h, transfection reagents were removed. Cells were then incubated with 6CEPN for 24 h, and supernatant fractions were collected for PGE2 measurement using an enzyme immunoassay kit (Cayman). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. (n = 4). The asterisks indicate a significant (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001) difference compared to each respective control group. B, 6CEPN targets COX-1 in HT29 cells. COX-1 proteins in HT29 cell lysates were pulled down and analyzed by Western blotting (left panels). 6CEPN inhibits PGE2 production in HT29 cells (right panels). Production of PGE2 was measured by ELISA. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. (n = 4). The asterisks (***) indicate a significant (p < 0.001) difference compared to control group. C, 6CEPN inhibits anchorage-independent growth of human colorectal cancer cells. HT29, HCT15 or DLD1 cells were grown in soft agar for 7 d and colonies counted as described in “Materials and Methods”. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. from 3 independent experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant (**, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.01) difference compared to each respective control group.