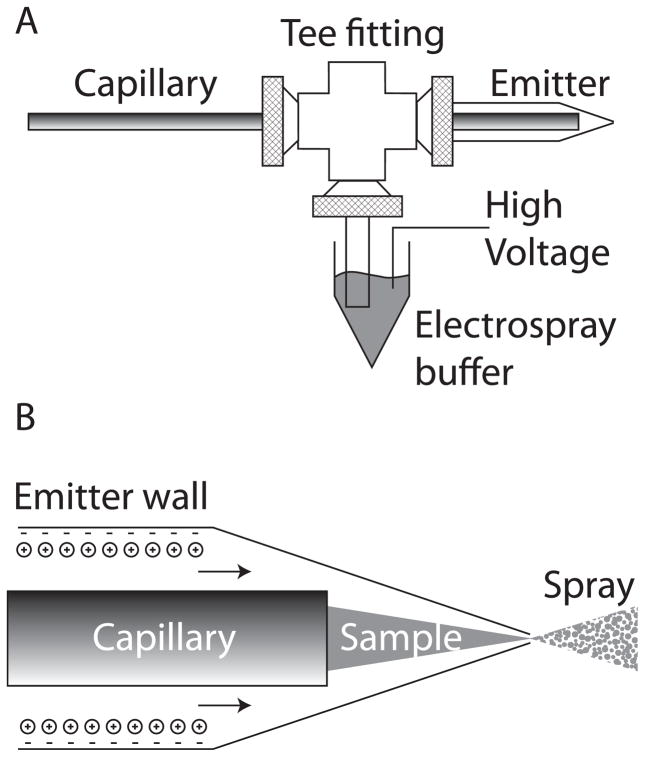
Figure 1.
Electrokinetically-pumped sheath-flow nanoelectrospray interface [19]. A – overview of the interface construction. The separation capillary is threaded through a plastic union into a borosilicate glass emitter. Plastic tubing is connected to a side arm and an electrospray buffer. High voltage is applied to that buffer to drive electrospray. The separation is driven by the difference in voltage applied to the two ends of the capillary. B – detail of the emitter. Anionic sites on the emitter wall attract a cations that form an electrical double layer. The electrospray potential drives these cations to the emitter tip; the cations drag buffer with them, creating electroosmotic flow. This electroosmotic flow ensheaths the sample stream as it exits the separation capillary. Electrospray is generated as the solution exits the emitter.