Figure 1. Prolonged cold ischemia promotes accelerated allograft rejection in anti-LFA-1 mAb treated recipients.
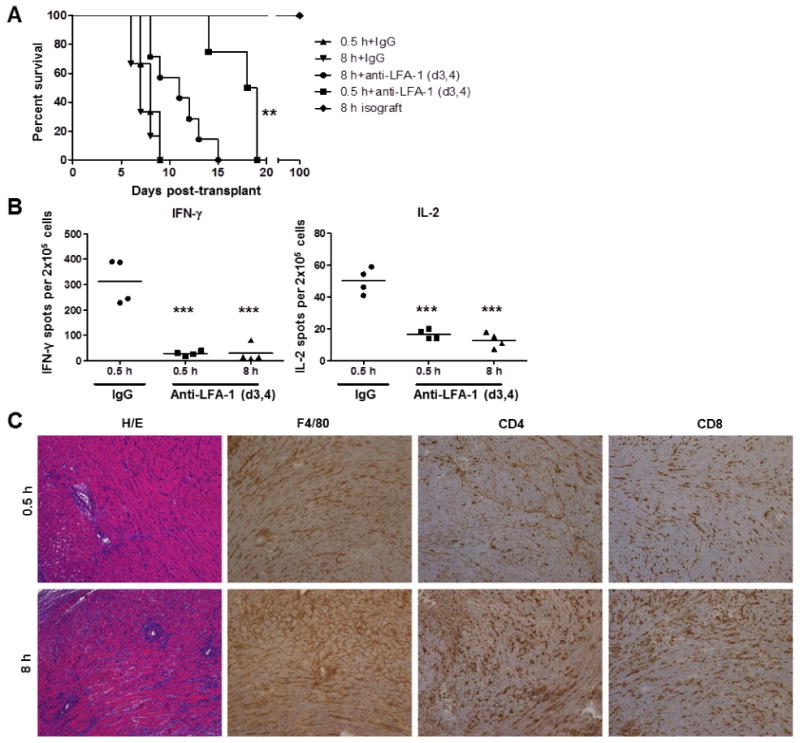
(A) Groups of 4-6 C57BL/6 recipient mice received syngeneic or complete MHC-mismatched A/J cardiac allografts subjected to minimal (0.5 h) or prolonged (8 h) cold ischemia and were treated with 200 μg control rat IgG or with anti-LFA-1 mAb on days 3 and 4 post-transplant. **p < 0.01 versus 8 h+anti-LFA-1 (d3,4), (B) Spleens were harvested from control and anti-LFA-1 mAb treated C57BL/6 allograft recipients on day 9 post-transplant. The number of donor-reactive splenocytes producing IFN-γ and IL-2 in each allograft recipient group was determined by ELISPOT assay. ***p < 0.001 (C) On day 12 post-transplant, cardiac allografts subjected to 0.5 or 8 h cold ischemia were harvested from C57BL/6 recipients treated with anti-LFA-1 mAb on days 3 and 4 post-transplant. Prepared sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin, anti-F4/80 mAb to detect macrophages, anti-CD4 mAb, or with anti-CD8 mAb. Magnification, 100×.
