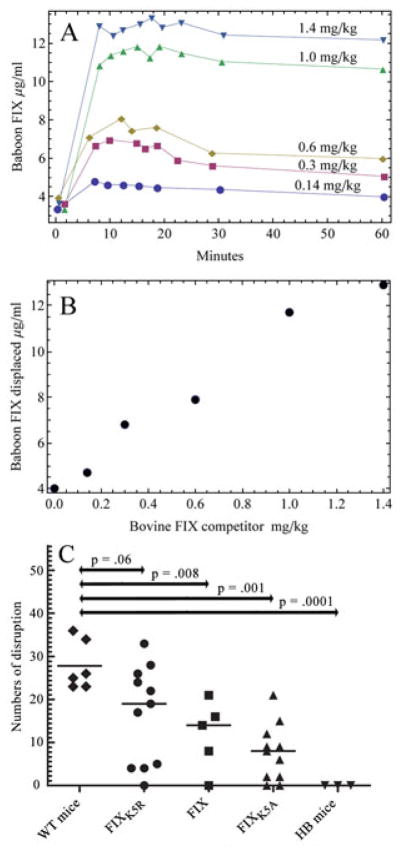
Figure 1.
(A) Figure 1A is from Stem DM, Knitter G, Kisiel W, Nawroth PP, In vivo evidence of intravascular binding sites coagulation factor IX, B J Haematology 1987;66:227–32. It is reproduced here with permission. It shows the amount of baboon FIX released into circulation following injection of bovine FIX at varying concentrations. (B) A replot of Figure 1A of the increase in baboon FIX in circulation at 10 minutes versus the amount of injected bovine FIX. (C) Haemophilia B mice received a bolus injection (0.9 mg/kg) of: FIXK5R, which binds tighter than wild-type to collagen IV, FIXWT, and FIXK5A which binds weaker than wild-type to collagen IV. Seven days after injection the ability of these molecules to promote haemostasis in a saphenous vein bleeding test [14] were compared to wild type and hemophilia B mice. The P-values are from a one-sided Mann-Whitney model. The P Value for FIXK5R vs FIXK5A was 0.003.