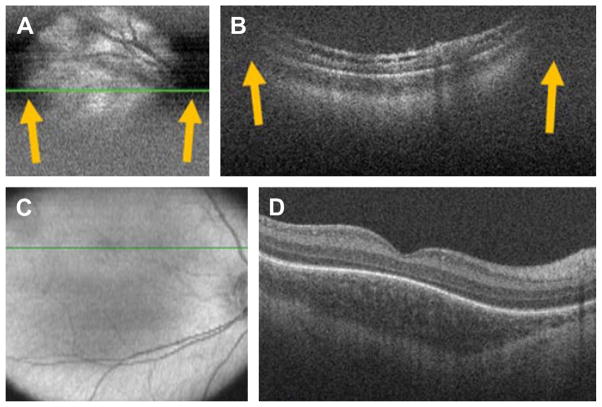
Fig. 5.
SDOCT clipping correction and focus adjustment. (A, B) SDOCT scanning without age-customized protocol. Severe clipping artifacts (white arrows) on the two-dimensional retinal image (A) and on the B-scan (B) of a 38-week-old PMA infant are noted in addition to poor image quality. (C, D) Images were obtained after applying the age-customized protocol. Improved field of view in the retinal image (C) and on the B-scan (D) with improved image quality. The inner retina in (B) shows schisis in an eye with peripheral retinal detachment. The fovea in (D) shows persisting inner retinal layers in an older premature infant. (From Maldonado RS, Izatt JA, Sarin N, et al. Optimizing hand-held spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging for neonates, infants and children. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51:2682; with permission.)