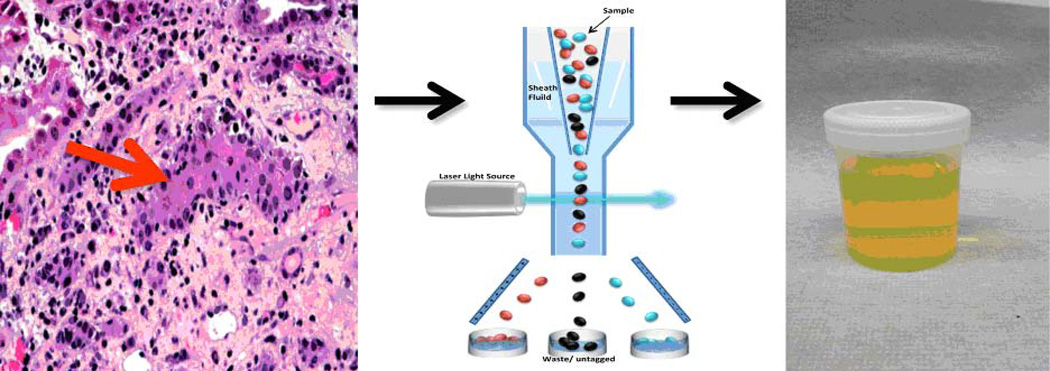
Fig. 1. Conceptualization of the kidney allograft as an in-vivo flow cytometer.
Interstitial inflammation and tubilitis are the histological hallmarks of ACR in the kidney allograft (left panel). Since ACR involves infiltration of T lymphocytes and additional cells into the tubular space, the kidney allograft is conceptualized to function as an in vivo flow cytometer (middle panel) facilitating the entry of graft destructive/protective T lymphocytes and other immune cells and graft parenchymal cells into the urinary space. In this formulation, urinary cell mRNA profiling reflects intragraft events deterministic of allograft status.