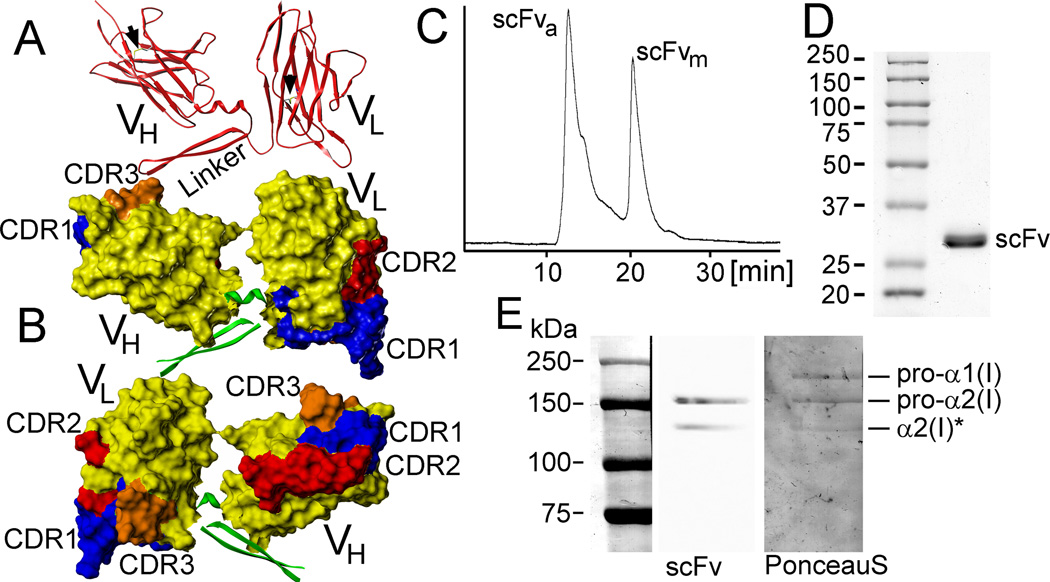
Figure 1.
Structural and functional analyses of the anti-α2Ct scFv construct. A, B: Computer models depicting the barrel-shaped immunoglobulin folds and organization of the CDRs. Arrows indicate predicted disulfide bonds formed within the variable regions (A). C: A chromatography profile indicates the presence of the aggregated (scFva) and monomeric (scFvm) forms of the scFv variant expressed in the presence of TMAO. D: Electrophoretic migration of the scFv variant indicating its expected mass of 28 kDa. E: Western blot assay of the binding of the scFv construct to the band corresponding to the intact pro-α2 chain of human procollagen I and its partially processed form (asterisk) indicates the specificity of this antibody variant to recognize the α2Ct epitope. The middle line (scFv) of panel E depicts a chemiluminescence-based image of procollagen I bands detected on the nitrocellulose membrane by the specific binding of the scFv variant. The right lane shows the same membrane stained with Ponceau S in which pro-α1 chains are also apparent.