Table 1.
Summary of ascarosides found in wild-type (N2) C. elegans culture medium that have had their structures confirmed through chemical synthesisa
| Structure-based name | Other name(s) | Orig. ref. | Mol. formula | [M+Na]+ | [M−H]− | n | R | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
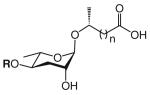
| Ascarosides with a saturated fatty acid side chain that is attached to the sugar at the penultimate (ω–1) carbon |
|
|||||||
| asc-C4 | ascr#11 | [7] | C10H18O6 | 257.1001 | 233.1025 | 1 | H | |
| asc-C5 | ascr#9 | [7,8] | C11H20O6 | 271.1158 | 247.1182 | 2 | H | |
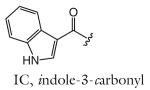
| IC-asc-C5 | indolecarboxyl- ascaroside C5; ascaroside C5; icas#S |
[6] | C20H25NO7 | 414.1529 | 390.1553 | 2 | IC | |
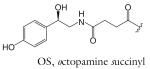
| OS-asc-C5 | osas#9 | [9] | C23H33NO10 | 506.2002 | 482.2026 | 2 | OS | |
| asc-C7 | daumone 1; ascr#l; ascaroside C7 |
[1] | C13H24O6 | 299.1471 | 275.1495 | 4 | H | |
| IC-asc-C7 | icas#l | [7,8] | C22H29NO7 | 442.1842 | 418.1866 | 4 | IC | |
| asc-C9 | ascr#10 | [7,8] | C15H28O6 | 327.1784 | 303.1808 | 6 | H | |
|
| ||||||||
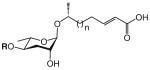
| Ascarosides with an α,β-unsaturated (Δ) fatty acid side chain that is attached to the sugar at the penultimate (ω–1) carbon | ||||||||
| asc-ΔC7 | ascr#7 | [5] | C13H22O6 | 297.1314 | 273.1339 | 2 | H |
|
| IC-asc-ΔC7 | icas #7 | [7,8] | C24H33NO7 | 440.1685 | 416.1709 | 2 | IC | |
| asc-ΔC9 | ascaroside C9; ascr#3; daumone 3 |
[2] | C15H26O6 | 325.1627 | 301.1651 | 4 | H | |
| IC-asc-ΔC9 | icas#3 | [7,8] | C24H31NO7 | 468.1998 | 444.2022 | 4 | IC | |
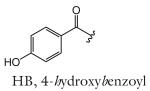
| HB-asc-ΔC9 | hbas#3 | [7] | C22H30O8 | 445.1838 | 421.1862 | 4 | HB | |
| MB-asc-ΔC9 | mbas#3 | [7] | C20H32O7 | 407.2046 | 383.2070 | 4 | MB | |
|
| ||||||||
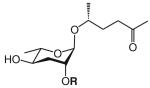
| Ascarosides with a side chain that is attached to the sugar at the penultimate (ω–1) carbon and terminates in a methyl ketone (MK)b | ||||||||
| asc-C6-MK | ascaroside C6; ascr#2; daumone 2 |
[2] | C12H22O5 | 269.1365 | n.a. | 2 | H |
|
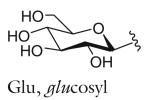
| Glu-asc-C6-MK | ascr#4; daumone 4 | [4] | C18H32O10 | 431.1893 | n.a. | 2 | Glu | |
|
| ||||||||
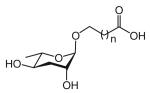
| Ascarosides with a saturated fatty acid side chain that is attached to the sugar at the terminal (ω) carbon | ||||||||
| asc-ωC3 | ascaroside C3; ascr#5; daumone 5 |
[3] | C9H16O6 | 243.0845 | 219.0869 | 1 | – |
|
| asc-ωC5 | oscr#9 | [7] | C11H20O6 | 271.1158 | 247.1182 | 3 | – | |
| asc-ωC9 | oscr#10 | [7] | C15H28O6 | 327.1784 | 303.1808 | 7 | – | |
|
| ||||||||
| Ascarosides with an α,β-unsaturated (Δ) side chain attached at the penultimate (ω–1) carbon and linked to p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) | ||||||||
| asc-ΔC7-PABA | ascr#8 | [5] | C20H27NO7 | n.a. | 392.1709 | 2 | - |
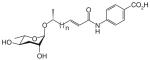
|
|
| ||||||||
| R group definitions: | ||||||||
|
|
|
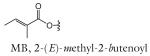
|
|
||||
The structure-based name given in the first column assumes that the canonical ascaroside structure is an ascaroside with a saturated fatty acid side chain that is attached to the sugar at the penultimate (ω–1) carbon. Deviations from the canonical structure are indicated such that each name conforms to the following: (modifications to the sugar)-asc-(deviations in the fatty acid)C#-(modifications at the end of the fatty acid)
Modifications to the sugar and their abbreviations are listed at the bottom of the table. Deviations in the fatty acid include attachment of the fatty acid to the sugar at the terminal (to) carbon, instead of penultimate (ω-1) carbon, as well as α-β (Δ) unsaturation of the fatty acid. Modifications at the end of the fatty acid include the methyl ketone (MK) moiety and addition of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
Many other ascarosides, such as asc-C6 (ascr#12), asc-C8 (ascr#14), IC-asc-C9 (icas#10), asc-Cll (ascr#18), asc-ωCll (oscr#18), asc-C12 (ascr#20), OS-asc-C9 (osas#10), and OS-asc-C6-MK (osas#2), have also been detected in wild-type C. elegans culture medium, but their structures have not yet been fully confirmed through chemical synthesis [7-9]
Reduced versions of asc-C6-MK (ascr#6.1 and ascr#6.2) with a hydroxyl instead of a ketone have also been reported [5]
