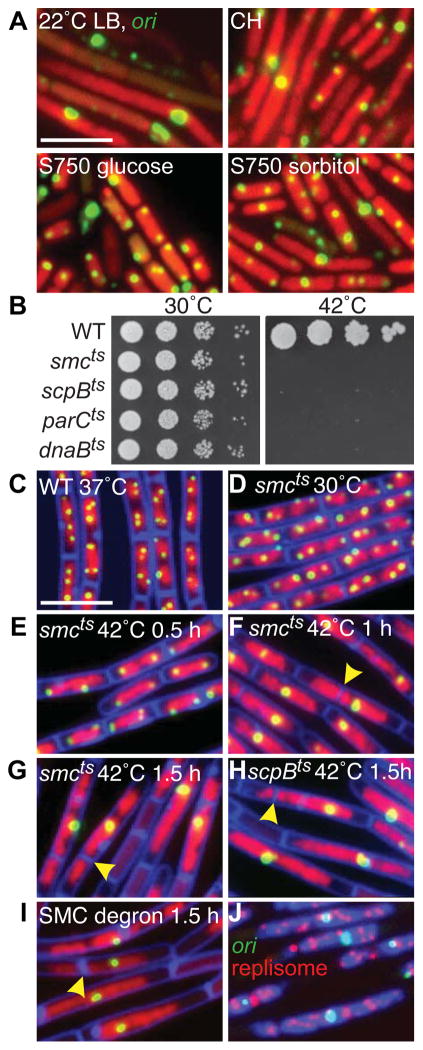
Figure 1. SMC complexes are required for origin segregation.
(A) Heterogeneous nucleoid morphologies and cell sizes in the SMC null mutant grown under permissive conditions. Representative images of Δsmc (strain BWX2208) grown at 22°C in LB, casein hydrolysates (CH), minimal medium (S750) supplemented with glucose or sorbitol. The nucleoids (red) and the origins (green) were visualized with HbsU-GFP and TetR-mCherry bound to a tetO array inserted adjacent to the origin. (B) Spot-dilutions of indicated temperature-sensitive mutants grown on LB-agar plates at permissive (30°C) and restrictive (42°C) temperatures. Representative images of DAPI-stained nucleoids (red) and origin foci (green) in wild-type cells (BWX811) grown in CH medium at 37°C (C); smcts (BWX2090) grown in CH medium at 30°C (D) and after shift to 42°C (E–G); scpBts (BWX2092) grown in CH medium for 1.5 h at 42°C (H); smc-ssrA (BWX1497) 1.5 h after induction of SspB grown in CH medium at 37°C (I). 85% (n=1273) of the smcts cells; 81% (n=1336) of the scpBts cells; and 85% (n=1392) of smc-ssrA cells had a single origin focus or cluster of foci at hour 1.5. Membranes (false-colored blue) were stained with FM4-64. Yellow carets highlight septum formation on top of the nucleoid. (J) Origin (green), replisome foci (red, DnaX-YFP), and DAPI-stained nucleoids (blue) in the smc-ssrA strain (BWX1771) 1.5 h after induction of SspB in CH medium at 37°C. Scale bars are 4 μm. Strains harboring wild-type copies of smc, scpB, or parC with a linked antibiotic resistance gene displayed normal chromosome organization and segregation when grown at 42°C (Figure S1F). See also Figure S1.