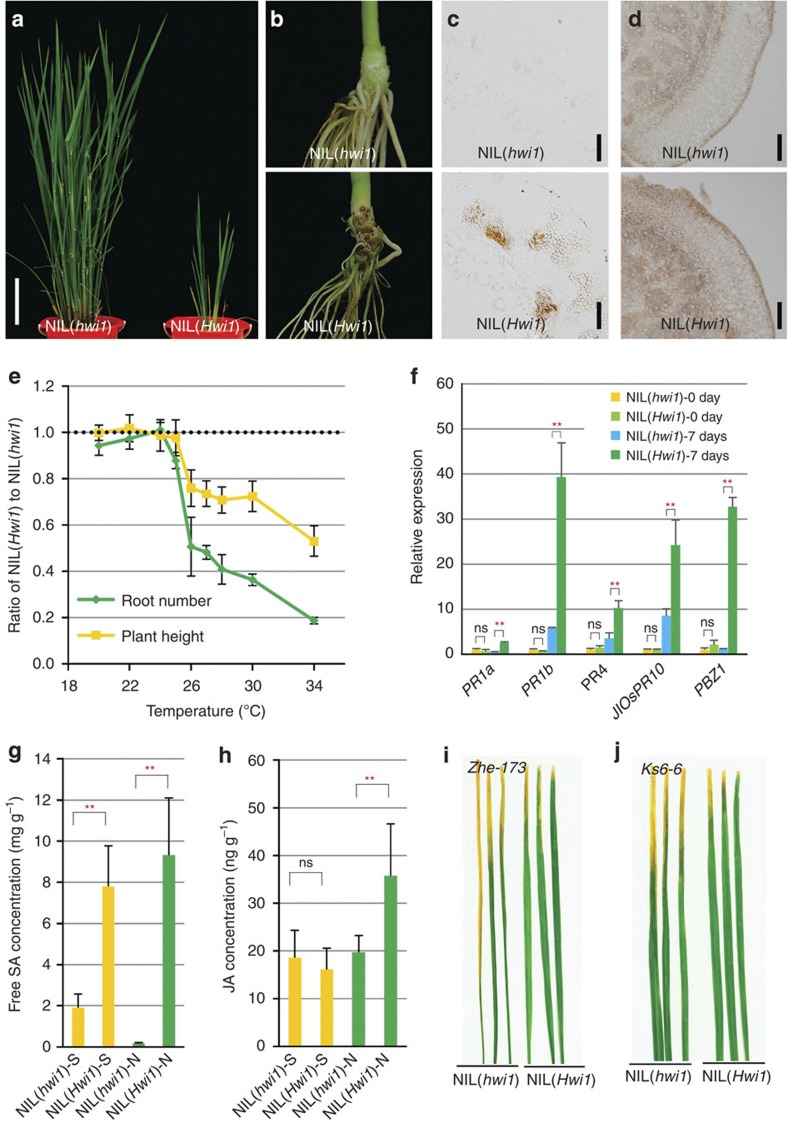
Figure 1. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of rice hybrid weakness.
(a) Morphology of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) at the booting stage. (b) Phenotype of the basal nodes of 30-day-old NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) plants. (c) Cross-sections of the basal nodes of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) plants without staining; scale bar, 200 μm. (d) TUNEL assay to detect PCD status of basal nodes from 8-day-old NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) seedlings; scale bar, 100 μm. (e) Effect of temperature treatments on the expression of hybrid weakness. (f) The expression of various PRs in the basal nodes of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) plants at 0 and 7 days after shifting from 20 to 30 °C. (g) The free salicylic acid content in leaf sheaths and basal nodes of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1). (h) The jasmonic acid content in leaf sheaths and basal nodes of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1). (i) The resistance of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) to bacterial pathogen Xoo strain Zhe-173 at the seedling stage. (j) The resistance of NIL(hwi1) and NIL(Hwi1) to bacterial pathogen Xoo strain Ks6-6 at the seedling stage. Error bars in (e–h) indicate s.d., n=10 (e), n=3 (f–h). **significant difference determined by the t-test at P<0.01; ns, not significant. S and N in (g) and (h) indicate leaf sheaths and basal nodes, respectively.