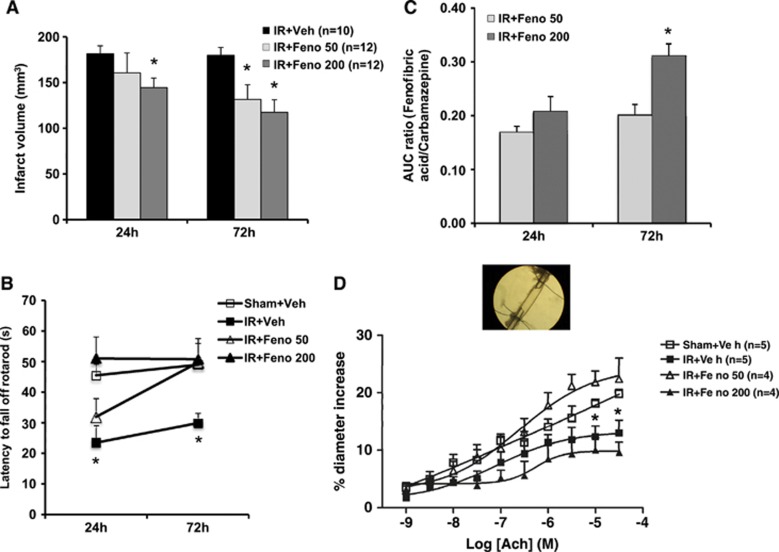
Figure 1.
Dose-effect study of fenofibrate. (A) Infarct volumes determined 24 and 72 hours after ischemia were lower in fenofibrate-treated rats (n=12) than in control rats (n=10). *P<0.05 vs. IR+Veh group. (B) The postischemia functional impairment (as evaluated in the rotarod test) was smaller in fenofibrate-treated rats (n=12) than in ischemic animals (n=10) 24 and 72 hours after the induction of cerebral ischemia. *P<0.05 vs. Sham+Veh group. (C) Plasmatic fenofibric acid increased in a dose-dependent manner at 24 and 72 hours. *P<0.05 vs. IR+Feno 50 group. (D) In vitro, the application of increasing concentrations of acetylcholine (ACh) to the middle cerebral artery led to endothelium-dependent relaxation, which was impaired in the aftermath of IR. This dysfunction was abolished in fenofibrate-treated rats at 50 mg/kg per day (n=4). *P<0.05 vs. Sham+Veh group. AUC, area under the curve; IR, ischemia/reperfusion.