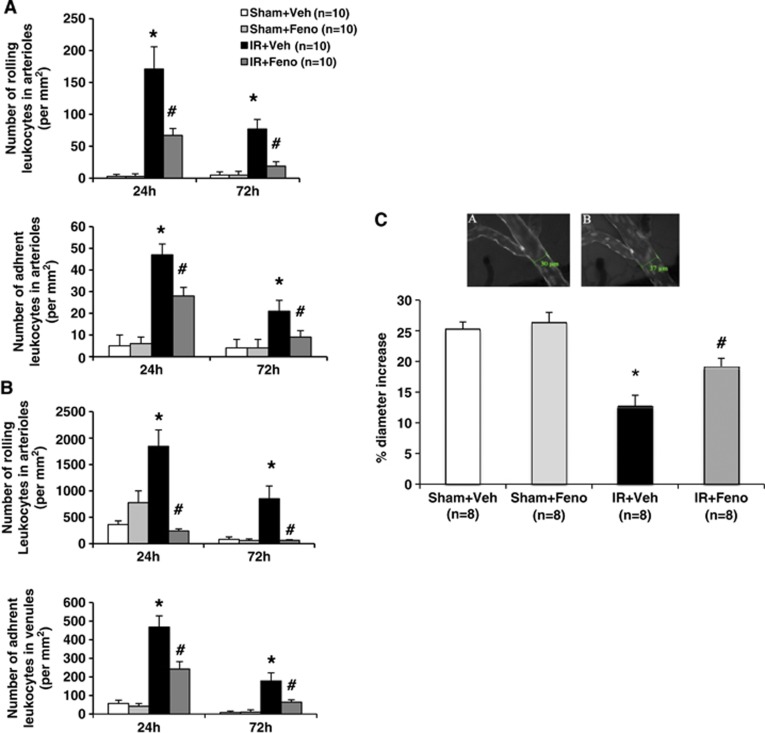
Figure 2.
Effects of treatment with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) agonist fenofibrate on interaction leukocyte–endothelium during the acute phase of cerebral ischemia and vascular reactivity in vivo. (A) In murine venules, fenofibrate treatment induced from 24 to 72 hours a significant decrease in leukocyte rolling and adhesion (n=10 per group); *P<0.05 vs. Sham+Veh group; #P<0.001 vs. IR+Veh group. (B) In murine arterioles, fenofibrate treatment induced from 24 to 72 hours a significant decrease in leukocyte rolling and adhesion (n=10 per group); *P<0.05 vs. Sham+Veh group; #P<0.001 vs. IR+Veh group. (C) In vivo, acetylcholine (ACh)-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation was determined by videomicroscopy of the murine pial arteries (A: the absence of ACh; B: the presence of ACh). The dysfunction in relaxation usually seen under ischemic conditions was abolished by fenofibrate treatment (n=8 per group). *P<0.05 vs. Sham+Veh group; #P<0.05 vs. IR+Veh group. Scale bar, 100 μm. IR, ischemia/reperfusion.