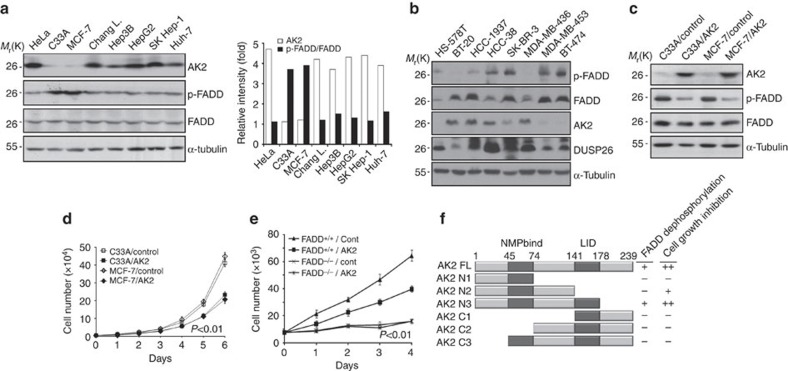
Figure 5. AK2 deficiency is detected in tumour cells with alteration in cell proliferation.
(a) AK2 expression is downregulated in MCF-7 and C33A tumour cells showing increased p-FADD. The expression profiles of AK2, FADD and p-FADD were examined in cancer cells by western blot analysis. Relative ratios (fold) of AK2 (open box) or p-FADD signal (filled box) to FADD on the blots were determined by densitometric analysis. (b) AK2 expression is downregulated in breast tumour cells showing increased level of p-FADD. The expression profiles of indicated proteins were examined in breast cancer cells by western blot analysis. (c) Reconstitution of C33A and MCF-7 cells with AK2 reduces FADD phosphorylation. C33A and MCF-7 cells were stably transfected with pcDNA3 (C33A/Control and MCF-7/Control) or AK2 (C33A/AK2 and MCF-7/AK2). Cell extracts were prepared and subjected to western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (d) Reconstitution of AK2 results in retardation of cell proliferation in C33A and MCF-7 tumour cells. Cell proliferation of C33A/Control, C33A/AK2, MCF-7/Control, and MCF-7/AK2 stable cells were examined for 6 days. Values are the mean±s.d. (n=3). P<0.01; t-test. (e) AK2 suppresses cell proliferation in wild-type MEFs but not in FADD−/− MEFs. FADD+/+ and FADD−/− MEFs (7 × 103) were transfected with either pcDNA (Cont) or pAK2-HA and the cell numbers were counted at different time points. Values are the mean±s.d. (n=3). P<0.01; t-test. (f) Functional dissection of AK2 domains responsible for FADD dephosphorylation and cell growth inhibition. A schematic diagram of the AK2 deletion mutants and a summary of the FADD dephosphorylation and the cell growth inhibition are described. All of AK2 constructs were fused with GFP.