Figure 1.
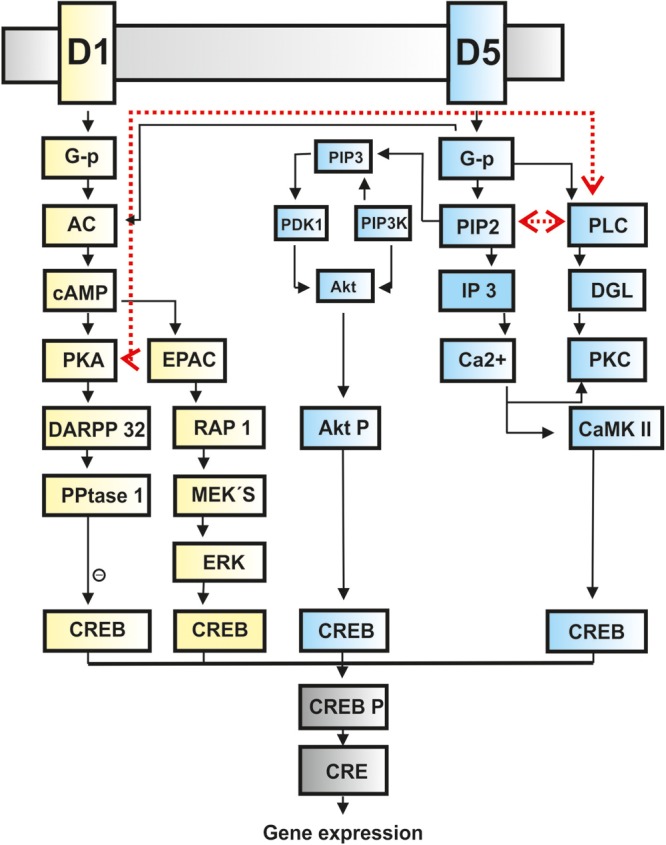
Signal cascades of D1 and D5 receptors. Schematic demonstration of the different molecular pathways of D1 (yellow boxes) and D5 receptors (blue boxes) ending in a common CREB activation (gray boxes). Crosstalk between the D1/D5 system is indicated by red dashed lines. An inhibitory effect is signified by a circle containing a minus symbol. Abbreviations: AC: adenylcyclase; AktP: Akt phosphorylated; CaMKII: calcium–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II; cAMP: cyclic 3′5′ adenosine monophosphate; CRE: cAMP response element; CREB: cAMP response element-binding protein; CREB P: CREB phosphorylated; DARPP-32: phosphoprotein of 32 kDa; DGL: diacylglycerol; D1: dopamine receptor 1; D5: dopamine receptor 5; EPAC: exchange protein activated by cAMP; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; G-p: G protein; IP3: inositol trisphosphate (IP3); by cAMP; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEK's: mitogen-activated kinases; PDK1: phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; PIP 2: phosphatidylinositol-4;5-bisphosphate; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol-3;4;5-triphosphate; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PKA: protein kinase A; PKC: protein kinase C; PLC: phospholipase C; PPtase 1: protein phosphatase 1; RAP 1: member of the RAS family of small GTP-binding proteins (Undieh 2010; Beaulieu and Gainetdinov 2011).
