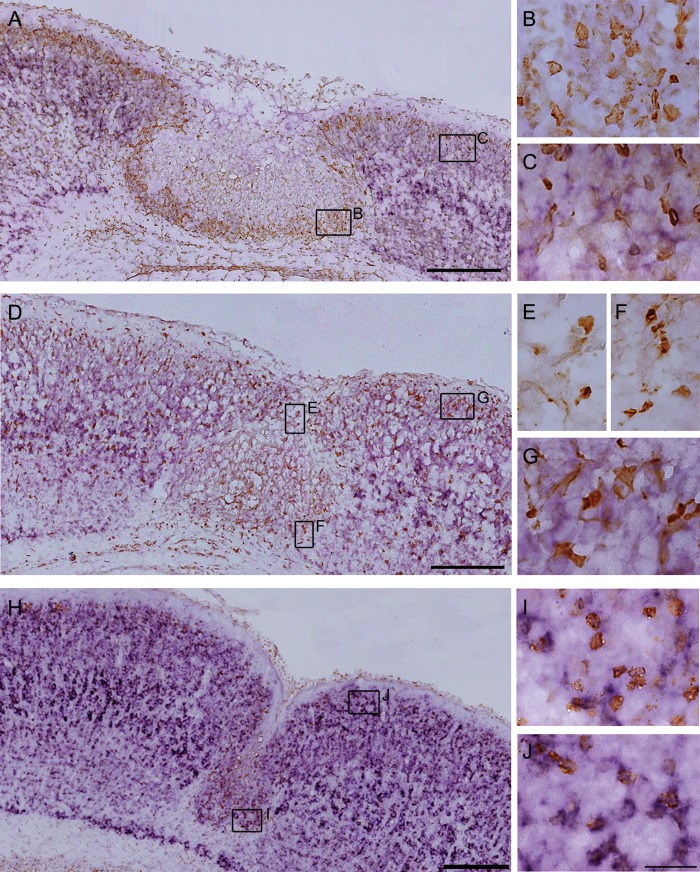
Figure 5.
Counterstaining of in situ hybridization for KCC2 mRNA with immunohistochemistry for BrdU or GFP. (A–C) In situ hybridization for KCC2 mRNA (purple) combined with immunostaining for BrdU (brown) on cryosections of a P4 FFL mouse cortex that received maternal injection of BrdU at E17.5. Higher magnification of BrdU-positive neurons in the area within 100 μm of the lesion site (B) and in the exofocal area >100 μm from the lesion border (C). Note that E17.5-born, BrdU-positive neurons accumulated in the area surrounding the necrotic tissue displayed less KCC2 mRNA expression (B) than those in the exofocal cortex (C). (D–G) In situ hybridization for KCC2 mRNA (purple) combined with immunostaining for heat-denatured GFP (brown) on cryosections of a P4 FFL mouse cortex. Higher magnification of GFP-positive neurons in the superficial part of the FFL (E), in the area surrounding the FFL (F), and in the exofocal area (G). Note that downregulation of KCC2 mRNA was detected in the GFP-positive GABAergic neurons in the superficial part of the FFL (E) and in the area surrounding the FFL (F), compared with that in the GABAergic neurons in the exofocal area (G). (H) In situ hybridization for KCC2 mRNA combined with immunostaining for BrdU on cryosections of a P7 FFL mouse cortex that received maternal injection of BrdU at E17.5. I and J show higher magnification of BrdU-positive neurons in layer 2 of the microgyric cortex (I) and in the exofocal cortex (J). There was no significant difference in KCC2 signals between the BrdU-positive neurons in the microgyric cortex (I) and those in the exofocal cortex (J). Scale bars: A, D, and H, 200 μm; B, C, E, F, G, I, and J, 25 μm.