Figure 12.
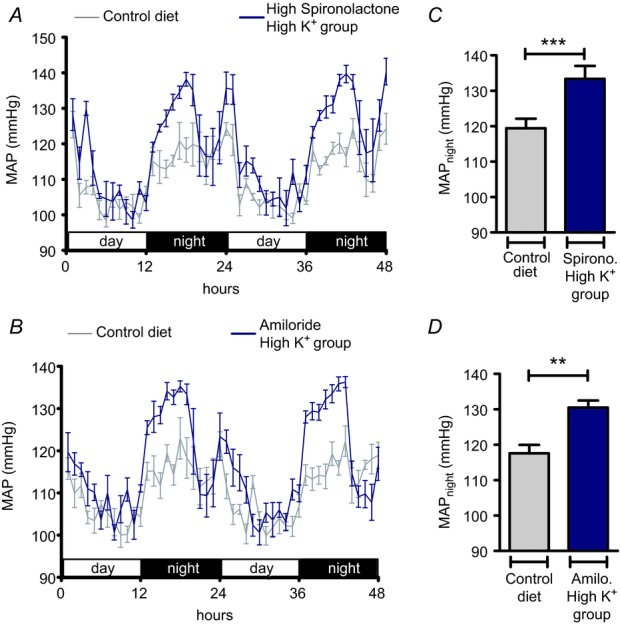
A, B, time course of mean arterial pressure (MAP) in mice in the high K+ (5% K+, 3% Na+) group treated with a high dosage of spironolactone (665 mg kg−1 per day; n = 4) or amiloride (4.8 mg kg−1 per day; n = 5) compared with MAP in mice fed control diet (0.93% K+, 0.24% Na+). C, D, MAPnight in mice fed control diet in comparison with MAPnight in mice in the high K+ (5% K+, 3% Na+) group additionally treated with spironolactone (C) or amiloride (D) (mean ± s.e.m; **P < 0.01,***P < 0.01, Student's paired t test). Blood pressure recordings were performed for 48 h before the experimental diet was started and again in the same mice at the end of the experimental period.
