Figure 5. Activity of lysyl oxidase (LOX) is increased in whole-lung tissues of chronically hypoxic mice and in culture media from human PASMC exposed to hypoxia or treated with CoCl2.
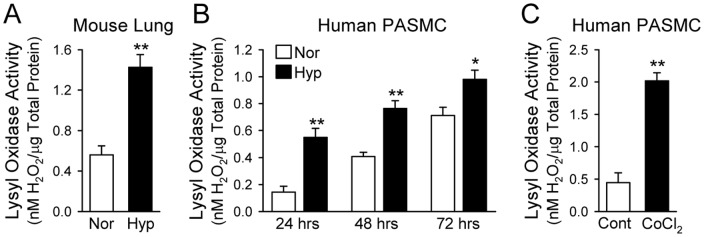
Enzymatic activity of LOX was determined using Fluorimetric Lysyl Oxidase Assay Kit by monitoring LOX-catalyzed H2O2 release from the fluorescent substrate in HRP-coupled reaction. A: LOX activity in lung tissue homogenates from normoxic (Nor, room air for 5 weeks, n = 5) and hypoxic (Hyp, 10% O2 for 5 weeks, n = 5) mice. **P<0.01 vs. Nor. B: LOX activity in culture media collected from human PASMC after 24, 48 and 72 hrs of exposure to normoxia (Nor, 21% O2) or hypoxia (Hyp, 3% O2). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Nor. C: LOX activity in culture media collected from PASMC treated with vehicle (Cont) or CoCl2 (100 µM for 48 hrs). **P<0.01 vs. Cont. Each bar graph displays the Cu-dependent activity of LOX determined by subtracting values obtained in the presence of BCS (a Cu chelator) from values in the absence of BCS. LOX activity is expressed in nanomoles of H2O2 released from the cells and normalized to the amount of total protein in each sample. Data are shown as mean±SE.
