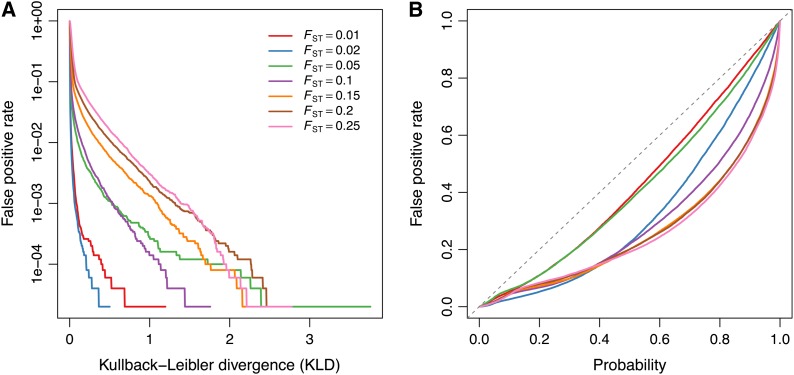
Figure 3.
(A) False-positive rate (neutral loci detected as outliers) as a function of the Kullback–Leibler divergence (KLD) threshold, for data sets 12–18. (B) False-positive rate, as a function of the quantile probability. For each data set analysis, pseudo-observed data (POD) are generated from the inference model with hyperparameters λ, πj, and Mi set to their respective posterior means, using a rejection-sampling algorithm (see File S2). The POD is then analyzed, using the same MCMC parameters (number and length of pilot runs, burn-in, chain length, etc.) as for the analysis of the original data. Each quantile probability defines a KLD threshold, which is used as a decision criterion for discriminating between neutral and selected markers.