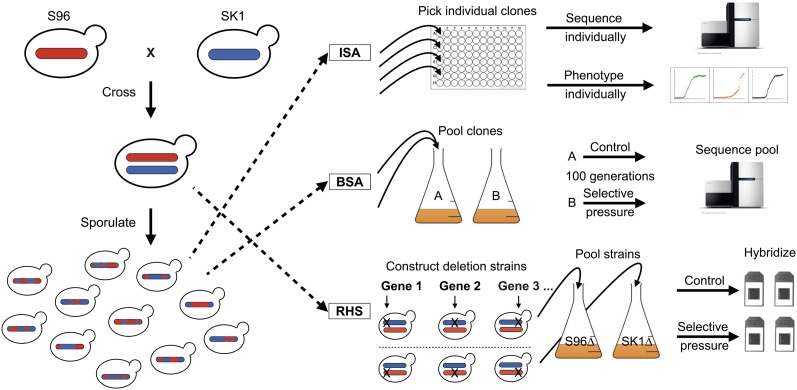
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the three QTL mapping approaches used in this study. The parental strain backgrounds S96 and SK1 were used for all approaches. ISA: genotyping and phenotyping are performed on individual segregants. BSA: a pool of segregants is grown in control and selective media. By sequencing the pooled genomic DNA, the allelic enrichments in the pool are determined. RHS: in a hybrid strain, alleles are alternatively deleted, resulting in reciprocal hemizygous, isogenic hybrid strains that differ only by a single allele. DNA barcodes specific to each gene enable the pooling and parallel analysis of strain fitness on a genome-wide level. After selective growth, the barcodes are amplified and hybridized to a microarray (or sequenced), providing a proxy of fitness that can be used to measure the effects of allelic variation in each gene on the phenotype of interest.